Characterization of actinide resin for separation of 51,52gMn from bulk target material
- PMID: 33725498
- PMCID: PMC8281445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2021.02.005
Characterization of actinide resin for separation of 51,52gMn from bulk target material
Abstract
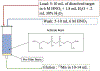
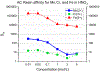
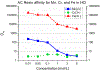
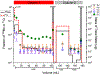
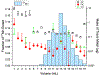
We report an extraction chromatography-based method via Actinide Resin for the isolation of radio-manganese from both natural chromium and isotopically enriched iron targets for cyclotron production of 52gMn and 51Mn. For the separation of 52gMn from natCr, a decay-corrected radiochemical yield of 83.7 ± 8.4% was achieved. For 51Mn from 54Fe, a decay-corrected radiochemical yield of 78 ± 11% was achieved. This automatable method efficiently isolates both radionuclides from accelerator target material.
Keywords: (51)Mn; (52g)Mn; Actinide resin; Extraction chromatography; Radionuclide production.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


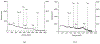

Similar articles
-
Solid phase extraction chromatography-based radiochemical isolation of cyclotron-produced 51Mn from enriched 54Fe targets.Nucl Med Biol. 2025 Mar-Apr;142-143:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108989. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Nucl Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39729887
-
Separation of gold from irradiated actinide material utilizing a 2- thenoyltrifluoroacetone extraction resin.J Chromatogr A. 2024 Jul 19;1727:464992. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2024.464992. Epub 2024 May 11. J Chromatogr A. 2024. PMID: 38761701
-
Radiochemical isolation method for the production of 52gMn from natCr for accelerator targets.Appl Radiat Isot. 2019 Apr;146:99-103. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.01.025. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Appl Radiat Isot. 2019. PMID: 30763821
-
Recent great impact by an Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) in nuclear and radiochemistry.J Med Invest. 2016;63(1-2):19-26. doi: 10.2152/jmi.63.19. J Med Invest. 2016. PMID: 27040048 Review.
-
A review on solid phase extraction of actinides and lanthanides with amide based extractants.J Chromatogr A. 2017 May 26;1499:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.03.035. Epub 2017 Mar 19. J Chromatogr A. 2017. PMID: 28408043 Review.
Cited by
-
Solid phase extraction chromatography-based radiochemical isolation of cyclotron-produced 51Mn from enriched 54Fe targets.Nucl Med Biol. 2025 Mar-Apr;142-143:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2024.108989. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Nucl Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 39729887
-
Developing ether and alcohol based extraction chromatography resins for purification of antimony-119 in nuclear medicine.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025 Aug 13;10(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s41181-025-00379-y. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2025. PMID: 40802155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Graves SA, Hernandez R, Fonslet J, England CG, Valdovinos HF, Ellison PA, Barnhart TE, Elema DR, Theuer CP, Cai W, Nickles RJ, and Severin GW, “Novel Preparation Methods of 52Mn for ImmunoPET Imaging”, Bioconjugate Chemistry, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 2118–2124, 2015, issn: 1043-1802. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00414. [Online]. Available: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00414. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fonslet J, Tietze S, Jensen AI, Graves SA, and Severin GW, “Optimized procedures for manganese-52: Production, separation and radiolabeling”, Applied Radiation and Isotopes, vol. 121, no. December 2016, pp. 38–43, 2017, issn: 18729800. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.11.021. [Online]. Available: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.11.021. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

