IgG4-related pleural effusion with high adenosine deaminase levels: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 33726002
- PMCID: PMC7982235
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025162
IgG4-related pleural effusion with high adenosine deaminase levels: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Levels of pleural fluid adenosine deaminase (ADA), a useful marker for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleurisy, are elevated in some reports of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related pleural effusion. We describe a patient with IgG4-related pleural effusion who exhibited a high concentration of ADA. Furthermore, we reviewed the literature to compare patients with IgG4-related pleural effusion and tuberculous pleurisy.
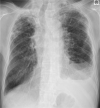
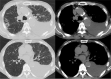
Patient concerns: A 75-year-old male patient had dyspnea for 1 month with a left pleural effusion that was exudative, lymphocyte dominant. The pleural fluid test results revealed a total protein (TP) concentration of 6.60 g/dl, a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level of 383 IU/dl, and an ADA concentration of 54.5 U/L. An interferon gamma release assay showed a negative result.
Diagnoses: Histological analysis of the thoracoscopic pleural biopsy revealed lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, with 80 IgG4-positive plasma cells/high-power field, and an IgG4/IgG ratio of approximately 40% to 50%. Other diseases were ruled out based on symptoms, negative autoimmune antigen results, and histopathologic findings. Thus, he was diagnosed with IgG4-related pleural effusion.
Interventions: He received 15 mg of prednisolone as therapy.
Outcomes: His pleural effusion and symptoms improved gradually within several months, and prednisolone was tapered to 6 mg daily.
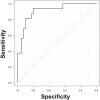
Lessons: It is important to distinguish between IgG4-related pleural effusion and tuberculous pleurisy. Therefore, we compared 22 patients with IgG4-related pleural effusion from PubMed and the Japan Medical Abstracts Society to 40 patients with tuberculous pleurisy at Fukujuji Hospital from January 2017 to May 2019. According to thoracentesis findings, 14 of 18 patients with IgG4-related pleural effusion had high ADA more than 40 U/L. The pleural effusion of patients with IgG4-related pleural effusion showed higher TP levels (P < .001) and lower LDH (P < .001) and ADA levels (P = .002) than those with tuberculous pleurisy. Moreover, the pleural fluid ADA/TP ratio was a good predictor for differentiating IgG4-related pleural effusion and tuberculous pleurisy (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.909; 95% confidence level: 0.824-0.994).
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-tuberculous, adenosine deaminase-positive lymphocytic pleural effusion: Consider immunoglobulin G4-related disease.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2020;37(2):225-230. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v37i2.9098. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2020. PMID: 33093787 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural effusion adenosine deaminase (ADA) level and occult tuberculous pleurisy.Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009 Oct;15(5):294-6. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19901882
-
Pleuritis associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease under normal thoracoscopic findings: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Apr 30;15(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02718-4. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33926544 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of adenosine deaminase in tuberculous pleurisy: a meta-analysis.Respir Med. 2008 May;102(5):744-54. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.12.007. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Respir Med. 2008. PMID: 18222681
-
Use of pleural fluid levels of adenosine deaminase and interferon gamma in the diagnosis of tuberculous pleuritis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2010 Jul;16(4):367-75. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e32833a7154. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2010. PMID: 20473171 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related Pleuritis Complicated with Minimal Change Disease.Intern Med. 2022 Mar 1;61(5):723-728. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7010-20. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 34483205 Free PMC article.
-
Curious case of the unexplained exudative pleural effusion.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Sep 20;14(9):e245796. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-245796. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34544724 Free PMC article.
-
Granzyme A as biomarker for diagnosis in tuberculous pleural effusion.JCI Insight. 2024 Dec 6;9(23):e185307. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.185307. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39641275 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of pleural effusion with a high adenosine deaminase level: a case-control study.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Sep 21;22(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02150-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36131272 Free PMC article.
-
A unique case of IgG4-related skin disease and sclerosing cholangitis in a patient with previous hepatitis exposure.JAAD Case Rep. 2021 Jul 24;15:52-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.008. eCollection 2021 Sep. JAAD Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34401431 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

