The predictive value of absolute lymphocyte counts on tumor progression and pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma
- PMID: 33726710
- PMCID: PMC7968315
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08004-2
The predictive value of absolute lymphocyte counts on tumor progression and pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: Differentiating true glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) from pseudoprogression (PsP) remains a challenge with current standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The objective of this study was to explore whether patients' absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) levels can be utilized to predict true tumor progression and PsP.
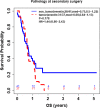
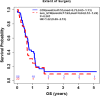
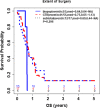
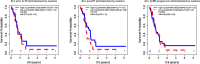
Methods: Patients were considered eligible for the study if they had 1) GBM diagnosis, 2) a series of blood cell counts and clinical follow-ups, and 3) tumor progression documented by both MRI and pathology. Data analysis results include descriptive statistics, median (IQR) for continuous variables and count (%) for categorical variables, p values from Wilcoxon rank sum test or Fisher's exact test for comparison, respectively, and Kaplan-Meier analysis for overall survival (OS). OS was defined as the time from patients' second surgery to their time of death or last follow up if patients were still alive.
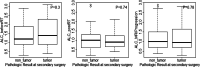
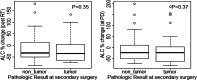
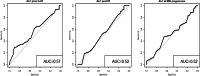
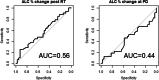
Results: 78 patients were included in this study. The median age was 56 years. Median ALC dropped 34.5% from baseline 1400 cells/mm3 to 917 cells/mm3 after completion of radiation therapy (RT) and temozolomide (TMZ). All study patients had undergone surgical biopsy upon MRI-documented progression. 37 had true tumor progression (47.44%) and 41 had pseudoprogression (52.56%). ALC before RT/TMZ, post RT/TMZ and at the time of MRI-documented progression did not show significant difference between patients with true progression and PsP. Although not statistically significant, this study found that patients with true progression had worse OS compared to those with PsP (Hazard Ratio [HR] 1.44, 95% CI 0.86-2.43, P = 0.178). This study also found that patients with high ALC (dichotomized by median) post-radiation had longer OS.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that ALC level in GBM patients before or after treatment does not have predictive value for true disease progression or pseudoprogression. Patients with true progression had worse OS compared to those who had pseudoprogression. A larger sample size that includes CD4 cell counts may be needed to evaluate the PsP predictive value of peripheral blood biomarkers.
Keywords: Absolute lymphocyte count; Glioblastoma; Prognosis; Pseudoprogression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Hysterectomy with radiotherapy or chemotherapy or both for women with locally advanced cervical cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 7;(4):CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD010260. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010260.pub3. PMID: 25847525 Updated.
-
Optimisation of chemotherapy and radiotherapy for untreated Hodgkin lymphoma patients with respect to second malignant neoplasms, overall and progression-free survival: individual participant data analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 13;9(9):CD008814. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008814.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28901021 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pilot trial of topical MTS‑01 application to reduce dermatitis in patients receiving chemoradiotherapy for stage I‑III carcinoma of the anal canal.Int J Oncol. 2022 Jun;60(6):68. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5358. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35438186 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative Immune-Inflammatory Status of the Patients With Newly-Diagnosed Glioblastoma - Could It Genuinely Predict Their Survival?Cureus. 2023 Aug 20;15(8):e43802. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43802. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37731450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mesfin FB, Al-Dhahir MA. Cancer, Brain Gliomas. StatPearls Publishing. 2019. - PubMed
-
- Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Stroup NE, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006-2010. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii1-56. 10.1093/neuonc/not151. Erratum in: Neuro Oncol. 2014 May;16(5):760. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

