Angiotensin II-induced upregulation of SGLT1 and 2 contributes to human microparticle-stimulated endothelial senescence and dysfunction: protective effect of gliflozins
- PMID: 33726768
- PMCID: PMC7967961
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01252-3
Angiotensin II-induced upregulation of SGLT1 and 2 contributes to human microparticle-stimulated endothelial senescence and dysfunction: protective effect of gliflozins
Abstract
Background: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors reduced cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes patients independently of glycemic control. Although angiotensin II (Ang II) and blood-derived microparticles are major mediators of cardiovascular disease, their impact on SGLT1 and 2 expression and function in endothelial cells (ECs) and isolated arteries remains unclear.
Methods: ECs were isolated from porcine coronary arteries, and arterial segments from rats. The protein expression level was assessed by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence staining, mRNA levels by RT-PCR, oxidative stress using dihydroethidium, nitric oxide using DAF-FM diacetate, senescence by senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity, and platelet aggregation by aggregometer. Microparticles were collected from blood of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD-MPs).
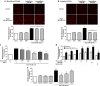
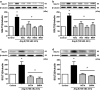
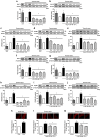
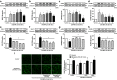
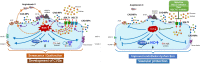
Results: Ang II up-regulated SGLT1 and 2 protein levels in ECs, and caused a sustained extracellular glucose- and Na+-dependent pro-oxidant response that was inhibited by the NADPH oxidase inhibitor VAS-2780, the AT1R antagonist losartan, sotagliflozin (Sota, SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor), and empagliflozin (Empa, SGLT2 inhibitor). Ang II increased senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity and markers, VCAM-1, MCP-1, tissue factor, ACE, and AT1R, and down-regulated eNOS and NO formation, which were inhibited by Sota and Empa. Increased SGLT1 and SGLT2 protein levels were observed in the rat aortic arch, and Ang II- and eNOS inhibitor-treated thoracic aorta segments, and were associated with enhanced levels of oxidative stress and prevented by VAS-2780, losartan, Sota and Empa. CAD-MPs promoted increased levels of SGLT1, SGLT2 and VCAM-1, and decreased eNOS and NO formation in ECs, which were inhibited by VAS-2780, losartan, Sota and Empa.
Conclusions: Ang II up-regulates SGLT1 and 2 protein expression in ECs and arterial segments to promote sustained oxidative stress, senescence and dysfunction. Such a sequence contributes to CAD-MPs-induced endothelial dysfunction. Since AT1R/NADPH oxidase/SGLT1 and 2 pathways promote endothelial dysfunction, inhibition of SGLT1 and/or 2 appears as an attractive strategy to enhance the protective endothelial function.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Circulating microparticles; Empagliflozin; Endothelial senescence and dysfunction; SGLT1; SGLT2.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG, Biberach, Germany.
Figures



References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56–28. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

