Gamma heavy chain disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case report
- PMID: 33726782
- PMCID: PMC7968189
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-021-02696-7
Gamma heavy chain disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Gamma heavy chain disease (γ-HCD) is a monoclonal gammopathy defined by an abnormal clonal and isolated production of incomplete heavy chain gamma (γ), unable to bind with light chains kappa or lambda. This disease is rare and remains poorly described. Its association to lymphoid neoplasm is well established, but exceptional forms of γ-HCD may also accompany auto-immune diseases. We report here a new case of γ-HCD characterized by an indolent course with a 4-year follow-up, and its association with quiescent rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
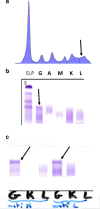
Case presentation: We report the case of a 85-year old French white man followed for quiescent anti-CCP+ rheumatoid arthritis treated by prednisolone 4 mg/day and hydroxychloroquine 200 mg/day since 10 years, and a monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance for 6 years, who was hospitalized for costal fractures after a fall. Serum protein electrophoresis showed a stable small monoclonal peak, and capillary electrophoresis/immunosubtraction technique identified an isolated clonal γ-heavy chain (HC). Bone marrow aspiration was normal and he had no other lymphoproliferation. The monoclonal peak remained stable after 4 years of follow-up.
Conclusions: In case of monoclonal peak without complete monoclonal Ig on serum protein electrophoresis, the diagnosis of γ-HCD should be discussed and capillary electrophoresis/immune-subtraction is a mean to detect isolated monoclonal heavy chain (HC). Gamma-HC disease is rare, may be associated to RA, and may have an indolent course.
Keywords: Capillary electrophoresis; Case report; Rheumatoid arthritis; γ-Heavy chain.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Wahner-Roedler DL, Witzig TE, Loehrer LL, Kyle RA. Gamma-heavy chain disease: review of 23 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 2003;82:236–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

