HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN): telerehabilitation using an unactuated device based on serious games improves the upper limb function in chronic stroke
- PMID: 33726801
- PMCID: PMC7961165
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-021-00841-3
HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN): telerehabilitation using an unactuated device based on serious games improves the upper limb function in chronic stroke
Abstract
Background: HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN) is an unactuated version of the robotic device ArmAssist combined with a telecare platform. Stroke patients are able to train the upper limb function using serious games at home. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of MERLIN training on the upper limb function of patients with unilateral upper limb paresis in the chronic phase of stroke (> 6 months post stroke).
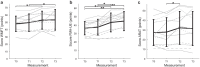
Methods: Patients trained task specific serious games for three hours per week during six weeks using an unactuated version of a robotic device. Progress was monitored and game settings were tailored through telerehabilitation. Measurements were performed six weeks pre-intervention (T0), at the start (T1), end (T2) and six weeks post-intervention (T3). Primary outcome was the Wolf Motor Function Test (WMFT). Secondary outcomes were other arm function tests, quality of life, user satisfaction and motivation.
Results: Twelve patients were included, ten completed the training. From start of the intervention to six weeks follow up, WMFT improved significantly with 3.8 points (p = .006), which is also clinically relevant. No significant changes in quality of life were observed. Patients were overall satisfied with the usability of the device. Comfort and the robustness of the system need further improvements.
Conclusion: Patients in the chronic phase of stroke significantly improved their upper limb function with the MERLIN training at home. Trial registration This study is registered at the Netherlands Trial Register (NL7535). Registered 18-02-2019, https://www.trialregister.nl/trial/7535 .
Keywords: Hand; Home training; Rehabilitation; Stroke; Task specific; Telerehabilitation; Training device; Upper limb.
Conflict of interest statement
Tecnalia R&I holds the IP of ArmAssist. AG and TK are employed at TECNALIA, San Sebastian, Spain, from which they receive financial compensation.
Figures

References
-
- Kwakkel G, Kollen BJ, van der Grond J, Prevo AJH. Probability of regaining dexterity in the flaccid upper limb. Stroke. 2003;34:2181–2186. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000087172.16305.CD. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

