Pneumonia in Infancy and Risk for Asthma: The Role of Familial Confounding and Pneumococcal Vaccination
- PMID: 33727032
- PMCID: PMC8411448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.03.006
Pneumonia in Infancy and Risk for Asthma: The Role of Familial Confounding and Pneumococcal Vaccination
Abstract
Background: Studies have reported an increased risk for asthma following lower respiratory tract infections, but few studies have specifically assessed this risk in children diagnosed with pneumonia in infancy. Furthermore, it is not fully understood whether this association is indicative of a causal relationship or if certain children have a predisposition for both diseases.
Research question: Are children diagnosed with pneumonia in infancy at increased risk for asthma, and what is the role of familial confounding and pneumococcal conjugate vaccine immunization on the association?
Study design and methods: This study was a nationwide register-based cohort analysis of > 900,000 Swedish children to assess the association between pneumonia in infancy and prevalent asthma at 4 years. A secondary aim was to assess if the association has changed after the introduction of nationwide pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) immunization as this has led to a shift in pneumonia etiology. The study controlled for important confounders, including shared environmental and familial confounding, by using sibling analyses.
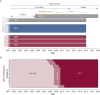
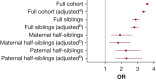
Results: There was a strong association between pneumonia diagnosis in infancy and prevalent asthma at 4 years (adjusted OR, 3.38; 95% CI, 3.26-3.51), as well as in the full sibling analyses (adjusted OR, 2.81; 95% CI, 2.58-3.06). The risk for asthma following pneumonia diagnosis in infancy was slightly higher for those born in the PCV period compared with the pre-PCV period (adjusted OR, 3.80 [95% CI, 3.41-4.24] vs 3.28 [95% CI, 3.15-3.42]) when the proportion of viral pneumonia etiology was also higher (14.5% vs 10.7%, respectively) and the overall asthma prevalence was lower (5.3% vs 6.6%).
Interpretation: Children diagnosed with pneumonia in infancy have a highly increased risk for prevalent asthma at 4 years, which might have implications for future asthma preventive measures and needs to be considered when assessing the morbidity that can be attributed to pneumonia.
Keywords: asthma; children; epidemiology; family design; pneumonia.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Asher M.I., Montefort S., Bjorksten B. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368(9537):733–743. - PubMed
-
- Papi A., Brightling C., Pedersen S.E., Reddel H.K. Asthma. Lancet. 2018;391(10122):783–800. - PubMed
-
- Blanken M.O., Rovers M.M., Molenaar J.M. Respiratory syncytial virus and recurrent wheeze in healthy preterm infants. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(19):1791–1799. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen S.F., van der Sluis S., Stensballe L.G. Exploring the association between severe respiratory syncytial virus infection and asthma: a registry-based twin study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179(12):1091–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

