Attention recruits frontal cortex in human infants
- PMID: 33727420
- PMCID: PMC7999871
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2021474118
Attention recruits frontal cortex in human infants
Abstract
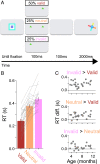
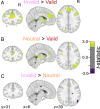
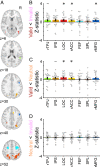
Young infants learn about the world by overtly shifting their attention to perceptually salient events. In adults, attention recruits several brain regions spanning the frontal and parietal lobes. However, it is unclear whether these regions are sufficiently mature in infancy to support attention and, more generally, how infant attention is supported by the brain. We used event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in 24 sessions from 20 awake behaving infants 3 mo to 12 mo old while they performed a child-friendly attentional cuing task. A target was presented to either the left or right of the infant's fixation, and offline gaze coding was used to measure the latency with which they saccaded to the target. To manipulate attention, a brief cue was presented before the target in three conditions: on the same side as the upcoming target (valid), on the other side (invalid), or on both sides (neutral). All infants were faster to look at the target on valid versus invalid trials, with valid faster than neutral and invalid slower than neutral, indicating that the cues effectively captured attention. We then compared the fMRI activity evoked by these trial types. Regions of adult attention networks activated more strongly for invalid than valid trials, particularly frontal regions. Neither behavioral nor neural effects varied by infant age within the first year, suggesting that these regions may function early in development to support the orienting of attention. Together, this furthers our mechanistic understanding of how the infant brain controls the allocation of attention.
Keywords: attentional cuing; early development; fMRI; frontoparietal network; gaze coding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gibson E. J., Exploratory behavior in the development of perceiving, acting, and the acquiring of knowledge. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 39, 1–42 (1988).
-
- Baillargeon R., Object permanence in 3-and 4-month-old infants. Dev. Psychol. 23, 655 (1987).
-
- Aslin R. N., Salapatek P., Saccadic localization of visual targets by the very young human infant. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 17, 293–302 (1975).
-
- Johnson M. H., Posner M. I., Rothbart M. K., Facilitation of saccades toward a covertly attended location in early infancy. Psychol. Sci. 5, 90–93 (1994).
-
- Farroni T., Massaccesi S., Pividori D., Johnson M. H., Gaze following in newborns. Infancy 5, 39–60 (2004).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

