Impact of corneal parameters, refractive error and age on density and morphology of the subbasal nerve plexus fibers in healthy adults
- PMID: 33727601
- PMCID: PMC7966734
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85597-5
Impact of corneal parameters, refractive error and age on density and morphology of the subbasal nerve plexus fibers in healthy adults
Abstract
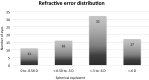
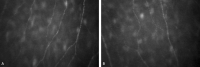
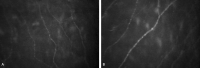
The purpose of this study was to analyze corneal sub-basal nerve plexus (SBNP) density and morphology and their relationships with corneal parameters and refractive status. In this single center study, in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) was performed in 76 eyes of 38 healthy subjects aged 19-87 (mean age 34.987 ± 1.148). Nerve fiber analysis was performed using Confoscan 4 microscope with semi-automated software (Nidek Technologies, Italy) The nerve fiber length (NFL) µm/mm2, nerve fiber density (NFD) no./mm2, tortuosity coefficient (TC), and nerve beadings density (NBD) no./mm were considered. Relationship between SBNP parameters and corneal curvature, thickness, diameter, and refraction were analyzed. Additionally, the association with gender, laterality and age were determined. NFL was inversely correlated with age (r = - 0.528, p < 0.001), myopic refractive error (spherical value) (r = - 0.423, p < 0.001), and cylindrical power (r = - 0.340, p = 0.003). NFD was inversely correlated with age (r = - 0.420, p < 0.001) and myopic refractive error (r = - 0.341, p = 0.003). NBD showed a low inverse correlation with cylindrical power (r = - 0.287, p = 0.012) and a slight positive correlation with K (r = 0.230, p = 0.047). TC showed a significant negative correlation between age (r = - 0.500, p < 0.001) and myopic refractive error (r = - 0.351, p = 0.002). Additionally, there were strong positive correlations between NFL and NFD (r = 0.523, p < 0.001), NFL and TI (r = 0.603, p < 0.001), and NFD and TC (r = 0.758, p < 0.001). Multiple regression analysis revealed age to be the most significant factor affecting SBNP density (B = - 0.467, p = 0.013) and length (B = - 61.446, p < 0.001); myopic refractive error reduced both SBNP density (B = - 2.119, p = 0.011) and length (B = - 158.433, p = 0.016), while gender and laterality had no significant effects (p > 0.005). SBNP fiber length decreases with age, myopic refractive error and cylindrical power. SBNP fiber density reduces with age and myopic refractive error. Corneal nerve parameters are not influenced by gender or laterality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

