Polystyrene microplastic contamination versus microplankton abundances in two lagoons of the Florida Keys
- PMID: 33727619
- PMCID: PMC7971037
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85388-y
Polystyrene microplastic contamination versus microplankton abundances in two lagoons of the Florida Keys
Abstract
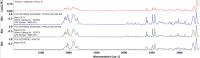
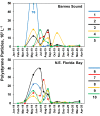
A microscopic study of microplankton in two coastal lagoons in the Florida Keys coincidently, and unexpectedly, revealed the widespread presence of high concentrations of polystyrene microplastic particles. The polystyrene particles were first observed in the second year of a 2-year study of phytoplankton communities, with peak densities in the spring/summer of 2019 at all ten sampling sites in the two lagoons. Polystyrene particle densities reached levels up to 76,000 L-1. The particles ranged in size from 33 to 190 µm, similar to the size range of microplanktonic algae (20-200 µm). Over the period of peak polystyrene densities, average particle densities were similar to average densities of microplanktonic algae cells. The latter observation highlights the potential significance of the microplastic particles for the ecology of the pristine waters of the Florida Keys, if they persist.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Microplastic fragment and fiber contamination of beach sediments from selected sites in Virginia and North Carolina, USA.Mar Pollut Bull. 2020 Feb;151:110869. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110869. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Mar Pollut Bull. 2020. PMID: 32056649
-
Microplastics in Tampa Bay, Florida: Abundance and variability in estuarine waters and sediments.Mar Pollut Bull. 2019 Nov;148:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.068. Epub 2019 Aug 10. Mar Pollut Bull. 2019. PMID: 31422308
-
The Genomic Capabilities of Microbial Communities Track Seasonal Variation in Environmental Conditions of Arctic Lagoons.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 12;12:601901. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.601901. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33643234 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental field evidence for transport of microplastic tracers over large distances in an alluvial aquifer.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Apr 15;408:124844. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124844. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33383455
-
Nationwide monitoring of microplastics in bivalves from the coastal environment of Korea.Environ Pollut. 2021 Feb 1;270:116175. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116175. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Environ Pollut. 2021. PMID: 33352481
Cited by
-
Microplastics at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations Had Minimal Impacts on Pelagic Zooplankton Communities in a Large In-Lake Mesocosm Experiment.Environ Sci Technol. 2024 Oct 29;58(43):19419-19428. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.4c05327. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Environ Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39418533 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing microplastic pollution vulnerability in a protected coastal lagoon in the Mediterranean Coast of Egypt using GIS modeling.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 4;15(1):11557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93329-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40185773 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of a microplastic mixture on wood frogs (Rana sylvatica) across multiple life stages in an outdoor mesocosm experiment.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2025 Feb 1;44(2):444-459. doi: 10.1093/etojnl/vgae037. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39919243 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

