Co-occurring medical conditions among individuals with ASD-associated disruptive mutations
- PMID: 33727758
- PMCID: PMC7958308
- DOI: 10.1080/02739615.2020.1741361
Co-occurring medical conditions among individuals with ASD-associated disruptive mutations
Abstract
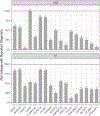
Children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are at risk for co-occurring medical conditions, many of which have also been reported among individuals with mutations in ASD-associated genes. This study examined rates of co-occurring medical conditions across 301 individuals with disruptive mutations to 1 of 18 ASD-risk genes in comparison to rates of conditions in an idiopathic ASD sample. Rates of gastrointestinal problems, seizures, physical anomalies, and immune problems were generally elevated, with significant differences in rates observed between groups. Results may inform medical care of individuals with ASD-associated mutations and research into mechanisms of co-occurring medical conditions in ASD.
Figures






References
-
- Adams DJ, Susi A, Erdie-Lalena CR, Gorman G, Hisle-Gorman E, Rajnik M, … & Nylund CM (2016). Otitis media and related complications among children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(5), 1636–1642. - PubMed
-
- Allen EK, Chen WM, Weeks DE, Chen F, Hou X, Mattos JL, … & Sale MM (2013). A genome-wide association study of chronic otitis media with effusion and recurrent otitis media identifies a novel susceptibility locus on chromosome 2. Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology, 14(6), 791–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. (2002). The medical home. Pediatrics, 110(1), 184–186. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
