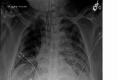
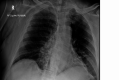
Coinfection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Bordetella bronchiseptica Pneumonia in a Renal Transplant Patient
- PMID: 33728132
- PMCID: PMC7935691
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.13113
Coinfection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Bordetella bronchiseptica Pneumonia in a Renal Transplant Patient
Abstract
Bordetella species cause respiratory infections in both humans and animals. Bordetella bronchiseptica (B. bronchiseptica) infection is an uncommon pathogen in humans. The clinical spectrum of infections with SARS-CoV-2 includes viral pneumonia of variable severity, with some patients developing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), requiring mechanical ventilation support. Transplant patients with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infection have high mortality. Bacterial coinfection, including pneumonia, have been described in patients with COVID-19. We present a renal transplant patient with COVID-19 pneumonia who developed B. bronchiseptica superinfection and had a rapid clinical and radiological response to azithromycin treatment.
Keywords: bordetella; covid-19; macrolide.
Copyright © 2021, Nagarakanti et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Dworkin MS, Sullivan PS, Buskin SE, Harrington RD, Olliffe J, MacArthur RD, Lopez CE. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28:1095–1099. - PubMed
-
- An unusual cause of cough and dyspnea in an immunocompromised patient. Berkowitz DM, Bechara RI, Wolfenden LL. Chest. 2007;131:1599–1602. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous