Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review
- PMID: 33728279
- PMCID: PMC7950424
- DOI: 10.1007/s40336-021-00419-y
Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Currently, there is an increasing interest regarding the impact of COVID-19 on the thyroid function. As several recent reports have described the onset of thyroid dysfunction in patients diagnosed with COVID-19, we performed a systematic review to assess the prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 as this information could be clinically relevant for the management of these patients.
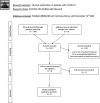
Methods: A comprehensive computer literature search using PubMed/Medline and Cochrane databases was performed until November 14, 2020 to search original articles evaluating thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19 patients. Information about thyroid dysfunction assessed by thyroid function test was retrieved by the eligible articles. Qualitative analysis (systematic review) only was performed whether a significant heterogeneity of data was detected.
Results: Seven studies including 1237 patients with COVID-19 were included. A significant heterogeneity across the studies was found. Most COVID-19 patients were euthyroid with TSH levels in the normal range (from 44 to 94% of the COVID-19 patients assessed in the included studies). The prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19 patients (defined as abnormal thyroid function tests) largely varies among the included studies between 13 and 64% of COVID-19 patients as well as clinical presentation. A positive correlation between thyroid dysfunction and clinical severity of COVID-19 was reported.
Conclusion: Literature data show that thyroid dysfunction is present in a significant percentage of patients with COVID-19. Assessment of thyroid function may be considered in symptomatic COVID-19 patients to have a baseline before introducing thyroid-interfering drugs and those requiring high-intensity care. Further, well-designed studies are needed to better elucidate the impact of COVID-19 on thyroid function and inform thyroid function testing and thyroid dysfunction management in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Systematic review; TSH; Thyroid; Thyroid dysfunction.
© Italian Association of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestLG is a member of the Roche Diagnostics advisory board and has received research grants and speaker honoraria from Roche Diagnostics, IBSA, and Sanofi-Genzyme. Other Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous