Population pharmacokinetic characteristics of cemiplimab in patients with advanced malignancies
- PMID: 33728546
- PMCID: PMC8225544
- DOI: 10.1007/s10928-021-09739-y
Population pharmacokinetic characteristics of cemiplimab in patients with advanced malignancies
Abstract
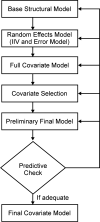
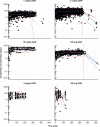
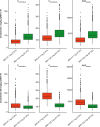
Cemiplimab, a human monoclonal antibody targeting programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor, demonstrated antitumor activity in patients with advanced malignancies and a safety profile comparable to other anti-PD-1 therapies. This population pharmacokinetics (PopPK) analysis of cemiplimab included 11,178 pharmacokinetics (PK) observations from 548 patients pooled from a first-in-human study (Study 1423; NCT02383212) in advanced malignancies and a Phase 2 study (Study 1540; NCT02760498) in advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC). Most patients (80.3%) received cemiplimab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (Q2W) intravenously (IV). A PopPK model was developed by evaluating two-compartment linear models with an empirical non-linear function describing time-varying change in cemiplimab clearance and covariates that improved goodness-of-fit. PopPK simulations were used to describe cemiplimab exposure generated by a fixed 350 mg every 3 weeks (Q3W) IV dose regimen. PopPK modeling showed that a two-compartment model with zero-order IV infusion rate and first-order elimination rate well described individual concentrations of cemiplimab. Although several covariates, including baseline body weight and albumin concentrations, had a modest impact on cemiplimab exposure, the magnitude of influence was within the typical observed PK variability of approximately 30%. Based on PopPK simulation results, the 350 mg Q3W dose regimen was selected for further studies in advanced malignancies, including advanced CSCC. Similarity in observed cemiplimab exposure at the fixed 350 mg Q3W and the weight-based 3 mg/kg Q2W dose regimens confirmed this fixed dose selection. A robust PopPK model was developed to describe cemiplimab concentrations and supported use of the fixed 350 mg Q3W IV dose regimen.
Keywords: Cemiplimab; Covariates; Fixed dose selection; Population modeling and simulations; Time-varying clearance.
Figures




References
-
- Burova E, Hermann A, Waite J, Potocky T, Lai V, Hong S, Liu M, Allbritton O, Woodruff A, Wu Q, D'Orvilliers A, Garnova E, Rafique A, Poueymirou W, Martin J, Huang T, Skokos D, Kantrowitz J, Popke J, Mohrs M, MacDonald D, Ioffe E, Olson W, Lowy I, Murphy A, Thurston G. Characterization of the anti-PD-1 antibody REGN2810 and its antitumor activity in human PD-1 knock-in mice. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16(5):861–870. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0665. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Migden MR, Rischin D, Schmults CD, Guminski A, Hauschild A, Lewis KD, Chung CH, Hernandez-Aya L, Lim AM, Chang ALS, Rabinowits G, Thai AA, Dunn LA, Hughes BGM, Khushalani NI, Modi B, Schadendorf D, Gao B, Seebach F, Li S, Li J, Mathias M, Booth J, Mohan K, Stankevich E, Babiker HM, Brana I, Gil-Martin M, Homsi J, Johnson ML, Moreno V, Niu J, Owonikoko TK, Papadopoulos KP, Yancopoulos GD, Lowy I, Fury MG. PD-1 blockade with cemiplimab in advanced cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(4):341–351. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1805131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (2021) LIBTAYO® [cemiplimab-rwlc] injection full US prescribing information. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/761097s007lbl.pdf. Accessed 23 Feb 2021
-
- European Medicines Agency (2019) LIBTAYO® EPAR. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/libtayo. Accessed 23 Feb 2021
-
- Fairman D, Narwal R, Liang M, Robbins PB, Schneider A, Chavez C, Lu H, Pak M, Blake-Haskins A, Vasselli J. Pharmacokinetics of MEDI4736, a fully human anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15_suppl):2602. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.2602. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

