Differential Effects of Wedelia chinensis on Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells
- PMID: 33729002
- PMCID: PMC7983241
- DOI: 10.1177/15347354211000119
Differential Effects of Wedelia chinensis on Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to Differential Effects of Wedelia chinensis on Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cellls.Integr Cancer Ther. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15347354251352682. doi: 10.1177/15347354251352682. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Integr Cancer Ther. 2025. PMID: 40567233 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive glioma, and its diffuse nature makes resection of it difficult. Moreover, even with the administration of postoperative radiotherapy and chemotherapy, prolonged remission is often not achieved. Hence, innovative or alternative treatments for GBM are urgently required. Traditional Chinese herbs and their functional components have long been used in the treatment of various cancers, including GBM. The current study investigated the antitumor activity of Wedelia chinensis and its major functional components, luteolin and apigenin, on GBM.
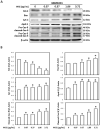
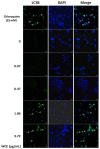
Materials and methods: MTT assay, Transwell migration assay, and flow cytometry analysis were adopted to assess the cell viability, invasive capability, and cell cycle. Immunofluorescence staining and Western blotting were used to detect the expressions of apoptotic and autophagy-related signaling molecules.
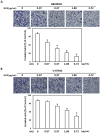
Results: The W. chinensis extract (WCE) significantly inhibited the proliferation and invasive ability of both GBM8401 and U-87MG cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, differential effects of WCE on GBM8401 and U-87MG cells were observed: WCE induced apoptosis in GBM8401 cells and autophagy in U-87MG cells. Notably, WCE had significant effects in reducing the cell survival and invasive capability of both GBM8401 and U-87MG cells than the combination of luteolin and apigenin.
Conclusions: Taken together, these findings indicate the potential of using WCE and the combination of luteolin and apigenin for GBM treatment. However, further investigations are warranted before considering recommending the clinical use of WCE or the combination of luteolin and apigenin as the standard for GBM treatment.
Keywords: Wedelia chinensis extract; apoptosis; autophagy; glioblastoma multiforme; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Batash R, Asna N, Schaffer P, Francis N, Schaffer M. Glioblastoma multiforme, diagnosis and treatment; recent literature review. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24:3002-3009. - PubMed
-
- Politsky JM. Brain tumor-related epilepsy: a current review of the etiologic basis and diagnostic and treatment approaches. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2017;17:70. - PubMed
-
- Cassileth BR. Evaluating complementary and alternative therapies for cancer patients. CA Cancer J Clin. 1999;49:362-375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

