Viral infections in humans and mice with genetic deficiencies of the type I IFN response pathway
- PMID: 33729549
- PMCID: PMC8900014
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.202048793
Viral infections in humans and mice with genetic deficiencies of the type I IFN response pathway
Abstract
Type I IFNs are so-named because they interfere with viral infection in vertebrate cells. The study of cellular responses to type I IFNs led to the discovery of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which also governs the response to other cytokine families. We review here the outcome of viral infections in mice and humans with engineered and inborn deficiencies, respectively, of (i) IFNAR1 or IFNAR2, selectively disrupting responses to type I IFNs, (ii) STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9, also impairing cellular responses to type II (for STAT1) and/or III (for STAT1, STAT2, IRF9) IFNs, and (iii) JAK1 and TYK2, also impairing cellular responses to cytokines other than IFNs. A picture is emerging of greater redundancy of human type I IFNs for protective immunity to viruses in natural conditions than was initially anticipated. Mouse type I IFNs are essential for protection against a broad range of viruses in experimental conditions. These findings suggest that various type I IFN-independent mechanisms of human cell-intrinsic immunity to viruses have yet to be discovered.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
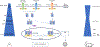
References
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147(927):258–67. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J, Valentine RC. Virus interference. II. Some properties of interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147(927):268–73. - PubMed
-
- Gresser I Production of interferon by suspensions of human leucocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961;108:799–803. - PubMed
-
- Gresser I Biologic effects of interferons. J Invest Dermatol. 1990;95(6 Suppl):66S–71S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R01 AI095983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI151663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143810/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R21 AI137371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI095983/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI088364/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127564/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG008956/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS072381/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

