Red seaweed (Asparagopsis taxiformis) supplementation reduces enteric methane by over 80 percent in beef steers
- PMID: 33730064
- PMCID: PMC7968649
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247820
Red seaweed (Asparagopsis taxiformis) supplementation reduces enteric methane by over 80 percent in beef steers
Abstract
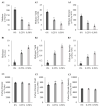
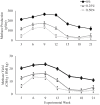
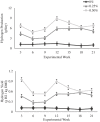
The red macroalgae (seaweed) Asparagopsis spp. has shown to reduce ruminant enteric methane (CH4) production up to 99% in vitro. The objective of this study was to determine the effect of Asparagopsis taxiformis on CH4 production (g/day per animal), yield (g CH4/kg dry matter intake (DMI)), and intensity (g CH4/kg ADG); average daily gain (ADG; kg gain/day), feed conversion efficiency (FCE; kg ADG/kg DMI), and carcass and meat quality in growing beef steers. Twenty-one Angus-Hereford beef steers were randomly allocated to one of three treatment groups: 0% (Control), 0.25% (Low), and 0.5% (High) A. taxiformis inclusion based on organic matter intake. Steers were fed 3 diets: high, medium, and low forage total mixed ration (TMR) representing life-stage diets of growing beef steers. The Low and High treatments over 147 days reduced enteric CH4 yield 45 and 68%, respectively. However, there was an interaction between TMR type and the magnitude of CH4 yield reduction. Supplementing low forage TMR reduced CH4 yield 69.8% (P <0.01) for Low and 80% (P <0.01) for High treatments. Hydrogen (H2) yield (g H2/DMI) increased (P <0.01) 336 and 590% compared to Control for the Low and High treatments, respectively. Carbon dioxide (CO2) yield (g CO2/DMI) increased 13.7% between Control and High treatments (P = 0.03). No differences were found in ADG, carcass quality, strip loin proximate analysis and shear force, or consumer taste preferences. DMI tended to decrease 8% (P = 0.08) in the Low treatment and DMI decreased 14% (P <0.01) in the High treatment. Conversely, FCE tended to increase 7% in Low (P = 0.06) and increased 14% in High (P <0.01) treatment compared to Control. The persistent reduction of CH4 by A. taxiformis supplementation suggests that this is a viable feed additive to significantly decrease the carbon footprint of ruminant livestock and potentially increase production efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Gerber PJ, Steinfeld H, Henderson B, Mottet A, Opio C, Dijkman J, et al. Tackling Climate Change through Livestock: A Global Assessment of Emissions and Mitigation Opportunities. FAO, Rome. 2013.
-
- Tomkins NW, Colegate SM, Hunter RA. A bromochloromethane formulation reduces enteric methanogenesis in cattle fed grain-based diets. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2009;49(12):1053–1058. 10.1071/EA08223 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

