A SBM-DEA based performance evaluation and optimization for social organizations participating in community and home-based elderly care services
- PMID: 33730070
- PMCID: PMC7968683
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248474
A SBM-DEA based performance evaluation and optimization for social organizations participating in community and home-based elderly care services
Abstract
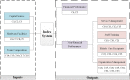
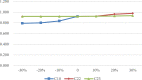
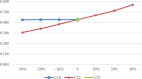
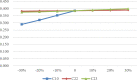
The community and home-based elderly care service system has been proved an effective pattern to mitigate the elderly care dilemma under the background of accelerating aging in China. In particular, the participation of social organizations in community and home-based elderly care service has powerfully fueled the multi-supply of elderly care. As the industry of the elderly care service is in the ascendant, the management lags behind, resulting in the waste of significant social resources. Therefore, performance evaluation is proposed to resolve this problem. However, a systematic framework for evaluating performance of community and home-based elderly care service centers (CECSCs) is absent. To overcome this limitation, the SBM-DEA model is introduced in this paper to evaluate the performance of CECSCs. 186 social organizations in Nanjing were employed as an empirical study to develop the systematic framework for performance evaluation. Through holistic analysis of previous studies and interviews with experts, a systematic framework with 33 indicators of six dimensions (i.e., financial management, hardware facilities, team building, service management, service object and organization construction) was developed. Then, Sensitivity Analysis is used to screen the direction of performance optimization and specific suggestions were put forward for government, industrial associations and CECSCs to implement. The empirical study shows the proposed framework using SBM-DEA and sensitivity analysis is viable for conducting performance evaluation and improvement of CECSCs, which is conducive to the sustainable development of CECSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

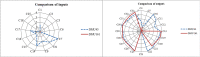
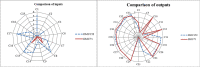
References
-
- WHO. World Report on Aging and Health. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2015. Available from: https://www.who.int/ageing/publications/world-report-2015/en/.
-
- Sun X, Liu X, Li F, Tao Y, Song Y. Comprehensive evaluation of different scale cities’ sustainable development for economy, society, and ecological infrastructure in China. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2017;163:S329–S327.
-
- Zhou JS, Walker A. The need for community care among older people in China. Ageing & Society. 2016;36(6):1312–1332. 10.1017/s0144686x15000343. WOS:000378595300010. - DOI
-
- Yuan J, Li L, Wang E, Skibniewski MJ. Examining sustainability indicators of space management in elderly Facilities—a case study in China. Journal of cleaner production. 2019;208:144–159.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

