Isolated middle mediastinal mass associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease
- PMID: 33730266
- PMCID: PMC7969669
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-021-01151-5
Isolated middle mediastinal mass associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Isolated middle mediastinal mass associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease.Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr 7;7(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40792-021-01168-w. Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33825993 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a multi-organ disorder predominantly occurring in middle-aged to elderly male patients characterized by multi-organ fibrosis, specific pathological findings of storiform fibrosis with IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration, and elevated serum IgG4 level. We herein report a rare presentation of IgG4-RD forming an isolated mass in the middle mediastinum mimicking a mediastinal tumor and discuss the clinical significance of mediastinal IgG4-RD.
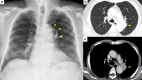
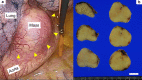
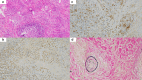
Case presentation: An 82-year-old male patient without any symptom was referred due to left middle mediastinal mass (3.8 × 2.4 cm). Because of suspected lymphoma, Castleman's disease, and lymphangitis due to tuberculosis, we performed a thoracoscopic resection for diagnosis and treatment. The mass was yellowish white with well-encapsulated, and storiform fibrosis with plasma cell infiltration, and obliterative phlebitis were observed microscopically. Additional immunohistochemical stain revealed IgG4-RD. Other radiological findings and serological results did not show evidence of other organs being affected from IgG4-RD nor autoimmune diseases. He is now followed at outpatient clinic without additional treatment for over a year, and an enhanced computed tomography does not show any recurrence.
Conclusion: It was a rare presentation of IgG4-RD forming isolated middle mediastinal mass, which suggests that we might suspect IgG4-RD for undetermined mediastinal mass in case of middle to elderly male patient.
Keywords: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease; mediastinal tumor; Systemic autoimmune disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis with an isolated scalp mass mimicking a brain tumor: a case report and literature review.J Rheum Dis. 2024 Jan 1;31(1):54-58. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2023.0023. Epub 2023 Jul 28. J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38130960 Free PMC article.
-
A case of IgG4-related anterior mediastinal sclerosing disease coexisting with autoimmune pancreatitis.Surg Case Rep. 2020 Jul 23;6(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s40792-020-00939-1. Surg Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32705358 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic dilemma of IgG4-related primary localized cervical lymphadenopathy associated with aberrant IL-6 expression level.Diagn Pathol. 2016 May 3;11(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13000-016-0493-3. Diagn Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27142509 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related periodontitis: case report and review of the literature.BMC Oral Health. 2021 May 28;21(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01592-2. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34049546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related hepatobiliary disease.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019 Nov;36(6):423-433. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31358425 Review.
Cited by
-
Extensive fibrosis in mediastinal seminoma is a diagnostic pitfall in small biopsies: two case reports.Mediastinum. 2022 Aug 22;7:6. doi: 10.21037/med-22-15. eCollection 2023. Mediastinum. 2022. PMID: 36926291 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Isolated middle mediastinal mass associated with immunoglobulin G4-related disease.Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr 7;7(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s40792-021-01168-w. Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33825993 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, Choi HK, Della-Torre E, Dicaire JF, et al. Members of the ACR/EULAR IgG4-RD Classification. Criteria Working Group The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:77–87. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216561. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

