Virological and immunological features of SARS-CoV-2-infected children who develop neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 33730580
- PMCID: PMC7962998
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108852
Virological and immunological features of SARS-CoV-2-infected children who develop neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
As the global COVID-19 pandemic progresses, it is paramount to gain knowledge on adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in children to define immune correlates of protection upon immunization or infection. We analyzed anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and their neutralizing activity (PRNT) in 66 COVID-19-infected children at 7 (±2) days after symptom onset. Individuals with specific humoral responses presented faster virus clearance and lower viral load associated with a reduced in vitro infectivity. We demonstrated that the frequencies of SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4+CD40L+ T cells and Spike-specific B cells were associated with the anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and the magnitude of neutralizing activity. The plasma proteome confirmed the association between cellular and humoral SARS-CoV-2 immunity, and PRNT+ patients show higher viral signal transduction molecules (SLAMF1, CD244, CLEC4G). This work sheds lights on cellular and humoral anti-SARS-CoV-2 responses in children, which may drive future vaccination trial endpoints and quarantine measures policies.
Keywords: Ab-mediated neutralization activity; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies; antigen-specific B cells; antigen-specific CD4 T cells; pediatric COVID-19; proteomic profiling.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
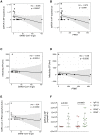
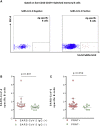

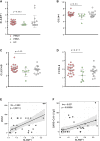

Comment in
-
BNT162B2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Heart and Lung Transplanted Young Adults: Is an Alternative SARS-CoV-2 Immune Response Surveillance Needed?Transplantation. 2022 Feb 1;106(2):e158-e160. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003999. Transplantation. 2022. PMID: 34954734 No abstract available.
References
-
- Altmann D.M., Boyton R.J. SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity: specificity, function, durability, and role in protection. Sci. Immunol. 2020;5:eabd6160. - PubMed
-
- Brodin P. Why is COVID-19 so mild in children? Acta Paediatr. 2020;109:1082–1083. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay P.K., Yu J., Roederer M. Live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell responses by CD154 expression. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

