Does Bone Mineral Density Differ between Fan-Beam and Pencil-Beam?: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
- PMID: 33730785
- PMCID: PMC7973396
- DOI: 10.11005/jbm.2021.28.1.67
Does Bone Mineral Density Differ between Fan-Beam and Pencil-Beam?: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
Abstract
Background: Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) has evolved from pencil-beam (PB) to narrow fan-beam (FB) densitometers. We performed a meta-analysis of the available observational studies to determine how different modes of DXA affect bone mineral density (BMD) measurements.
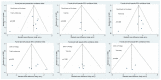
Methods: A total of 1,233 patients (808 women) from 14 cohort studies were included. We evaluated the differences in BMD according to the DXA mode: PB and FB. Additionally, we evaluated the differences in BMD between the 2 types of FB mode: FB (Prodigy) and the most recent FB (iDXA). Pairwise meta-analysis was performed, and weighted mean differences (WMD) were calculated for (total lumbar, total hip, and total body).
Results: No significant difference was observed in total lumbar (pooled WMD, -0.013; P=0.152) and total hip BMD (pooled WMD, -0.01; P=0.889), between PB and FB. However, total body BMD was significantly lower in the PB compared to the FB group (pooled WMD, -0.014; P=0.024). No significant difference was observed in lumbar BMD (pooled WMD, -0.006; P=0.567), total hip (pooled WMD, -0.002; P=0.821), and total body (pooled WMD, 0.015; P=0.109), between Prodigy and iDXA.
Conclusions: The results of this study warrant the recommendation that correction equations should not be used when comparing BMD from different modes. Further research is still needed to highlight the ways in which differences between DXA systems can be minimized.
Keywords: Absorptiometry, photon; Bone density; Densitometry; Osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Byung-Ho Yoon has been the associate editor of the Journal of Bone Metabolism since 2018. Yong-Chan Ha has been the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Bone Metabolism since 2017. No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
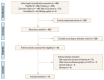


Similar articles
-
Differences between dual X-ray absorptiometry using pencil beam and fan beam modes and their determinants in vivo and in vitro.J Clin Densitom. 2000 Summer;3(2):157-66. doi: 10.1385/jcd:3:2:157. J Clin Densitom. 2000. PMID: 10871910
-
Total body and regional bone mineral densitometry (BMD) and soft tissue measurements: correlations of BMD parameter to lumbar spine and hip.Calcif Tissue Int. 2000 Aug;67(2):111-5. doi: 10.1007/s00223001124. Calcif Tissue Int. 2000. PMID: 10920214
-
Evaluation of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry bone mineral measurement--comparison of a single-beam and fan-beam design: the effect of osteophytic calcification on spine bone mineral density.Calcif Tissue Int. 1995 Mar;56(3):192-5. doi: 10.1007/BF00298608. Calcif Tissue Int. 1995. PMID: 7750022
-
A meta-analysis of fracture risk and bone mineral density in patients with systemic sclerosis.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;39(4):1181-1189. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04847-0. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31838641
-
Meta-analysis of walking for preservation of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women.Bone. 2008 Sep;43(3):521-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.05.012. Epub 2008 May 26. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18602880
References
-
- Albano D, Agnollitto PM, Petrini M, et al. Operator-related errors and pitfalls in dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: how to recognize and avoid them. Acad Radiol. 2020 http://dx.doi.og/10.1016/j.acra.2020.07.028. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

