Triazoloacridone C-1305 impairs XBP1 splicing by acting as a potential IRE1α endoribonuclease inhibitor
- PMID: 33730996
- PMCID: PMC7968329
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-021-00255-y
Triazoloacridone C-1305 impairs XBP1 splicing by acting as a potential IRE1α endoribonuclease inhibitor
Abstract
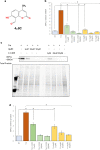
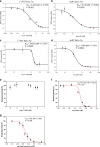
Inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α) is one of three signaling sensors in the unfolding protein response (UPR) that alleviates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in cells and functions to promote cell survival. During conditions of irrevocable stress, proapoptotic gene expression is induced to promote cell death. One of the three signaling stressors, IRE1α is an serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease (RNase) that promotes nonconventional splicing of XBP1 mRNA that is translated to spliced XBP1 (XBP1s), an active prosurvival transcription factor. Interestingly, elevated IRE1α and XBP1s are both associated with poor cancer survival and drug resistance. In this study, we used next-generation sequencing analyses to demonstrate that triazoloacridone C-1305, a microtubule stabilizing agent that also has topoisomerase II inhibitory activity, dramatically decreases XBP1s mRNA levels and protein production during ER stress conditions, suggesting that C-1305 does this by decreasing IRE1α's endonuclease activity.
Keywords: ER stress; IRE1α; UPR; XBP1s.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Genome-wide mRNA profiling identifies X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) as an IRE1 and PUMA repressor.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):7061-7080. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03952-1. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34636989 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of XBP1 splicing by inhibition of IRE1α is a promising therapeutic option in multiple myeloma.Blood. 2012 Jun 14;119(24):5772-81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-366633. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22538852 Free PMC article.
-
ER stress and distinct outputs of the IRE1α RNase control proliferation and senescence in response to oncogenic Ras.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 12;114(37):9900-9905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701757114. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28847931 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple roles of the unfolded protein response regulator IRE1α in cancer.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Sep;58(9):1623-1630. doi: 10.1002/mc.23031. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31041814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond UPR: cell-specific roles of ER stress sensor IRE1α in kidney ischemic injury and transplant rejection.Kidney Int. 2023 Sep;104(3):463-469. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.06.016. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 37391039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combined anticancer therapy with imidazoacridinone analogue C-1305 and paclitaxel in human lung and colon cancer xenografts-Modulation of tumour angiogenesis.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(14):3950-3964. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17430. Epub 2022 Jun 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35701366 Free PMC article.
-
Proteotoxic Stress as an Exploitable Vulnerability in Cells with Hyperactive AKT.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 21;22(21):11376. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111376. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768807 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mRNA profiling identifies X-box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) as an IRE1 and PUMA repressor.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Nov;78(21-22):7061-7080. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03952-1. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34636989 Free PMC article.
-
The hypoxia-induced changes in miRNA-mRNA in RNA-induced silencing complexes and HIF-2 induced miRNAs in human endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2022 Jul;36(7):e22412. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101987R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35713587 Free PMC article.
-
Old drugs, new challenges: reassigning drugs for cancer therapies.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Mar 5;30(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00710-0. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40038587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

