Intranasal administration of a recombinant RBD vaccine induced protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in mouse
- PMID: 33731271
- PMCID: PMC7934688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.006
Intranasal administration of a recombinant RBD vaccine induced protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in mouse
Abstract
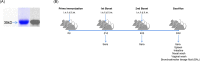
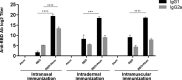
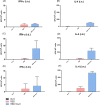
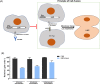
The emergence of the global Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic underscores the importance of the rapid development of a non-invasive vaccine that can be easily administered. A vaccine administered by nasal delivery is endowed with such characteristics against respiratory viruses. In this study, we generated a recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD)-based subunit vaccine. Mice were immunized via intranasal inoculation, microneedle-intradermal injection, or intramuscular injection, after which the RBD-specific immune responses were compared. Results showed that when administrated intranasally, the vaccine elicited a robust systemic humoral immunity with high titers of IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies as well as a significant mucosal immunity. Besides, antigen-specific T cell responses were also analyzed. These results indicated that the non-invasive intranasal administration should be explored for the future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine design.
Keywords: Intranasal administration; Mucosal immunity; Neutralizing antibody; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

