Ultrafast functional profiling of RNA-seq data for nonmodel organisms
- PMID: 33731361
- PMCID: PMC8015844
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.269894.120
Ultrafast functional profiling of RNA-seq data for nonmodel organisms
Abstract
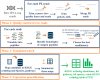
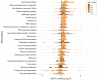
Computational time and cost remain a major bottleneck for RNA-seq data analysis of nonmodel organisms without reference genomes. To address this challenge, we have developed Seq2Fun, a novel, all-in-one, ultrafast tool to directly perform functional quantification of RNA-seq reads without transcriptome de novo assembly. The pipeline starts with raw read quality control: sequencing error correction, removing poly(A) tails, and joining overlapped paired-end reads. It then conducts a DNA-to-protein search by translating each read into all possible amino acid fragments and subsequently identifies possible homologous sequences in a well-curated protein database. Finally, the pipeline generates several informative outputs including gene abundance tables, pathway and species hit tables, an HTML report to visualize the results, and an output of clean reads annotated with mapped genes ready for downstream analysis. Seq2Fun does not have any intermediate steps of file writing and loading, making I/O very efficient. Seq2Fun is written in C++ and can run on a personal computer with a limited number of CPUs and memory. It can process >2,000,000 reads/min and is >120 times faster than conventional workflows based on de novo assembly, while maintaining high accuracy in our various test data sets.
© 2021 Liu et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
