BRD4S interacts with viral E2 protein to limit human papillomavirus late transcription
- PMID: 33731454
- PMCID: PMC8139696
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02032-20
BRD4S interacts with viral E2 protein to limit human papillomavirus late transcription
Abstract
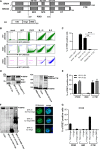
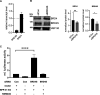
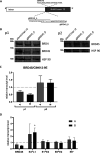
The E2 protein encoded by human papillomaviruses (HPV) is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that recruits viral and cellular proteins. Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) is a highly conserved interactor for E2 proteins that has been linked to E2's functions as transcription modulator, activator of viral replication and segregation factor for viral genomes. In addition to BRD4, a short form of BRD4 (BRD4S) is expressed from the BRD4 gene which lacks the C-terminal domain of BRD4. E2 proteins interact with the C-terminal motif (CTM) of BRD4, but a recent study suggested that the phospho-dependent interaction domain (PDID) and the basic interaction domain (BID) in BRD4 also bind to E2. These domains are also present in BRD4S. We now find that HPV31 E2 interacts with the isolated PDID domain in living cells and also with BRD4S which is present in detectable amounts in HPV-positive cell lines and is recruited into HPV31 E1 and E2 induced replication foci. Overexpression and knockdown experiments surprisingly indicate that BRD4S inhibits activities of E2. In line with that, the specific knockdown of BRD4S in the HPV31-positive CIN612-9E cell line induces mainly late viral transcripts. This occurs only in undifferentiated but not differentiated cells in which the productive viral replication cycle is induced. These data suggest that the BRD4S-E2 interaction is important to prevent HPV late gene expression in undifferentiated keratinocytes which may contribute to immune evasion and HPV persistence.ImportanceHuman papillomaviruses (HPV) have coevolved with their host by using cellular factors like bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) to control viral processes such as genome maintenance, gene expression and replication. We here show that, in addition to the C-terminal motif in BRD4, the phospho-dependent interaction domain in BRD4 interacts with E2 proteins which enable the recruitment of BRD4S, the short isoform of BRD4, to E2. Knock-down and overexpression of BRD4S reveals that BRD4S is a negative regulator of E2 activities. Importantly, the knockdown of BRD4S induces mainly L1 transcripts in undifferentiated CIN612-9E cells, which maintain replicating HPV31 genomes. Our study reveals an inhibitory role of BRD4S on HPV transcription, which may serve as an immune escape mechanism by the suppression of L1 transcripts and thus contribute to the establishment of persistent HPV infections.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SETD6 Regulates E2-Dependent Human Papillomavirus Transcription.J Virol. 2022 Nov 23;96(22):e0129522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01295-22. Epub 2022 Oct 27. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36300937 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of a Conserved Tyrosine in the Papillomavirus E2 Protein Regulates Brd4 Binding and Viral Replication.J Virol. 2019 May 1;93(10):e01801-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01801-18. Print 2019 May 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30842331 Free PMC article.
-
The E8E2C protein, a negative regulator of viral transcription and replication, is required for extrachromosomal maintenance of human papillomavirus type 31 in keratinocytes.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(3):1178-86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.3.1178-1186.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10627528 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Brd4 in different steps of the papillomavirus life cycle.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.12.006. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27965149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of viral replication and transcription by the papillomavirus E8^E2 protein.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27825778 Review.
Cited by
-
SETD6 Regulates E2-Dependent Human Papillomavirus Transcription.J Virol. 2022 Nov 23;96(22):e0129522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01295-22. Epub 2022 Oct 27. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36300937 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus associated cervical lesion: pathogenesis and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2023 Sep 14;4(5):e368. doi: 10.1002/mco2.368. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37719443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial and Functional Organization of Human Papillomavirus Replication Foci in the Productive Stage of Infection.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0268421. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02684-21. Epub 2021 Nov 9. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34749533 Free PMC article.
-
The Functions of BET Proteins in Gene Transcription of Biology and Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 3;8:728777. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.728777. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34540900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FACT subunit SUPT16H associates with BRD4 and contributes to silencing of interferon signaling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 26;50(15):8700-8718. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac645. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35904816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grassmann K, Rapp B, Maschek H, Petry KU, Iftner T. 1996. Identification of a differentiation-inducible promoter in the E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) in raft cultures of a new cell line containing high copy numbers of episomal HPV-16 DNA. J Virol 70:2339–2349. 10.1128/JVI.70.4.2339-2349.1996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

