Islet neogenesis associated protein (INGAP) protects pancreatic β cells from IL-1β and IFNγ-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 33731692
- PMCID: PMC7969959
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00441-z
Islet neogenesis associated protein (INGAP) protects pancreatic β cells from IL-1β and IFNγ-induced apoptosis
Abstract
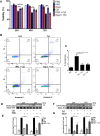
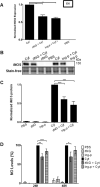
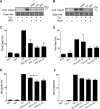
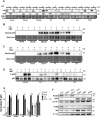
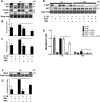
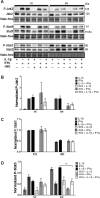
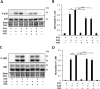
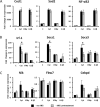
The goal of this study was to determine whether recombinant Islet NeoGenesis Associated Protein (rINGAP) and its active core, a pentadecapeptide INGAP104-118 (Ingap-p), protect β cells against cytokine-induced death. INGAP has been shown to induce islet neogenesis in diabetic animals, to stimulate β-cell proliferation and differentiation, and to improve islet survival and function. Importantly, Ingap-p has shown promising results in clinical trials for diabetes (phase I/II). However, the full potential of INGAP and its mechanisms of action remain poorly understood. Using rat insulinoma cells RINm5F and INS-1 treated with interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), we demonstrate here that both rINGAP and Ingap-p inhibit apoptosis, Caspase-3 activation, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and nitric oxide (NO) production, and explore the related signaling pathways. As expected, IL-1β induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), p38, and JNK signaling, whereas interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) activated the JAK2/STAT1 pathway and potentiated the IL-1β effects. Both rINGAP and Ingap-p decreased phosphorylation of IKKα/β, IkBα, and p65, although p65 nuclear translocation was not inhibited. rINGAP, used for further analysis, also inhibited STAT3, p38, and JNK activation. Interestingly, all inhibitory effects of rINGAP were observed for the cytokine cocktail, not IL-1β alone, and were roughly equal to reversing the potentiating effects of INFγ. Furthermore, rINGAP had no effect on IL-1β/NF-κB-induced gene expression (e.g., Ccl2, Sod2) but downregulated several IFNγ-stimulated (Irf1, Socs1, Socs3) or IFNγ-potentiated (Nos2) genes. This, however, was observed again only for the cytokine cocktail, not IFNγ alone, and rINGAP did not inhibit the IFNγ-induced JAK2/STAT1 activation. Together, these intriguing results suggest that INGAP does not target either IL-1β or IFNγ individually but rather inhibits the signaling crosstalk between the two, the exact mechanism of which remains to be investigated. In summary, our study characterizes the anti-inflammatory effects of INGAP, both protein and peptide, and suggests a new therapeutic utility for INGAP in the treatment of diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

