Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water Alleviates Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 33732014
- PMCID: PMC7956896
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S288289
Drinking Hydrogen-Rich Water Alleviates Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain Through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
Introduction: Chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain (CINP) is one of the most common complications of chemotherapeutic drugs which limits the dose and duration of potentially life-saving anticancer treatment and compromises the quality of life of patients. Our previous studies have reported that molecular hydrogen (H2) can be used to prevent and treat various diseases. But the underlying mechanism remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to explore the effects of hydrogen-rich water on gut microbiota in CINP.
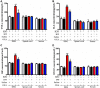
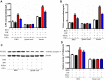
Methods: All C57BL/6J mice were divided into 4 groups: The group fed with normal drinking water and injected with saline (H2O + Saline), the group fed with normal drinking water and injected with oxaliplatin (H2O + OXA), the group fed with hydrogen-rich water and injected with saline (HW + Saline), and the group fed with hydrogen-rich water and injected with oxaliplatin (HW + OXA). The mechanical paw withdrawal threshold of the mice was tested on days 0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 after hydrogen-rich water treatment. On day 20, feces of mice from different groups were collected for microbial community diversity and structure analysis. The levels of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6), oxidative stress factors (OH- and ONOO-), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) were detected in dorsal root ganglia (DRG), L4-6 spinal cord segments and serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The expression of TLR4 in DRG and spinal cords was determined by Western blot.
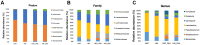
Results: The results illustrated that hydrogen-rich water could alleviate oxaliplatin-induced hyperalgesia, reduce the microbial diversity and alter the structure of gut microbiota, reverse the imbalance of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress, and decrease the expression of LPS and TLR4.
Conclusion: Hydrogen-rich water may alleviate CINP by affecting the diversity and structure of the gut microbiota, and then the LPS-TLR4 pathway, which provides a direction for further research.
Keywords: CINP; LPS-TLR4 pathway; gut microbiota; hydrogen-rich water.
© 2021 Lian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates hyperalgesia and reduces cytokines in rats with post-herpetic neuralgia via activating autophagy].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;33(2):155-8. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29762002 Chinese.
-
Oxaliplatin Regulates Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain in the Dorsal Horn and Dorsal Root Ganglion via the Calcineurin/NFAT Pathway.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(8):1197-1207. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180525091158. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29793414
-
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation-Mediated Rebalancing of the Gut-Brain Axis Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Sep 27. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00267. Online ahead of print. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39329364
-
Hydrogen-rich saline controls remifentanil-induced hypernociception and NMDA receptor NR1 subunit membrane trafficking through GSK-3β in the DRG in rats.Brain Res Bull. 2014 Jul;106:47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Brain Res Bull. 2014. PMID: 24951883
-
Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in cancer: animal models and related research progress.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1609791. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1609791. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of ingestion of hydrogen-dissolved alkaline electrolyzed water on stool consistency and gut microbiota: a double-blind randomized trial.Med Gas Res. 2021 Oct-Dec;11(4):138-144. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.318858. Med Gas Res. 2021. PMID: 34213495 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The gut microbiota-neuroimmune crosstalk and neuropathic pain: a scoping review.Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2023 Jun 19;4:e10. doi: 10.1017/gmb.2023.7. eCollection 2023. Gut Microbiome (Camb). 2023. PMID: 39295900 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Therapy for Cisplatin-Induced Allodynia and Dysfunctional and Emotional Impairments in Male and Female Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;12(12):2063. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122063. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136183 Free PMC article.
-
New Treatment for the Cognitive and Emotional Deficits Linked with Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;11(12):2387. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122387. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552595 Free PMC article.
-
DGKζ in Glycerophospholipid Metabolism Regulates the DAG and PA Balance and Interacts With PTEN to Alleviate Brain Damage in Septic Mice With Hydrogen Inhalation: A Comparative Metabolomic and Phosphoproteomic Analysis.Brain Behav. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70761. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70761. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40792381 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

