APOE-ε4 Carrier Status and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients With Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 33732104
- PMCID: PMC7959830
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.619051
APOE-ε4 Carrier Status and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients With Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
Background: Alternations in gut microbiota and a number of genes have been implicated as risk factors for the development of Alzheimer disease (AD). However, the interactions between the altered bacteria and risk genetic variants remain unclear.
Objective: We aimed to explore associations of the risk genetic variants with altered gut bacteria in the onset of AD.
Methods: We collected baseline data and stool and blood samples from 30 AD patients and 47 healthy controls in a case-control study. The rs42358/rs4512 (ApoE), rs3851179 (PICALM), rs744373 (BIN1), rs9331888 (CLU), rs670139 (MS4A4E), rs3764650 (ABCA7), rs3865444 (CD33), rs9349407 (CD2AP), rs11771145 (EPHA1), and rs3818361/rs6656401 (CR1) were sequenced, and microbiota composition was characterized using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. The associations of the altered gut bacteria with the risk genetics were analyzed.
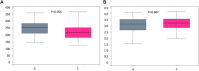
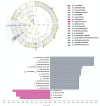
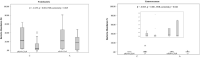
Results: Apolipoprotein ε4 allele and rs744373 were risk loci for the AD among 12 genetic variants. Phylum Proteobacteria; orders Enterobacteriales, Deltaproteobacteria, and Desulfovibrionales; families Enterobacteriaceae and Desulfovibrionaceae; and genera Escherichia-Shigella, Ruminococcaceae_UCG_002, Shuttleworthia, Anaerofustis, Morganelia, Finegoldia, and Anaerotruncus were increased in AD subjects, whereas family Enterococcaceae and genera Megamonas, Enterococcus, and Anaerostipes were more abundant in controls (P < 0.05). Among the altered microbiota, APOE ε4 allele was positively associated with pathogens: Proteobacteria.
Conclusion: The interaction of APOE ε4 gene and the AD-promoting pathogens might be an important factor requiring for the promotion of AD. Targeting to microbiota might be an effective therapeutic strategy for AD susceptible to APOE ε4 allele. This needs further investigation.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; apolipoprotein E; dysbiosis; genetic variants; gut microbiome.
Copyright © 2021 Hou, Xu, Ran, Luo and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of GWAS-linked loci with late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a northern Han Chinese population.Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Sep;9(5):546-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Alzheimers Dement. 2013. PMID: 23232270
-
rs3851179 Polymorphism at 5' to the PICALM Gene is Associated with Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases in Brazilian Population.Neuromolecular Med. 2017 Sep;19(2-3):293-299. doi: 10.1007/s12017-017-8444-z. Epub 2017 May 31. Neuromolecular Med. 2017. PMID: 28567584
-
Alzheimer risk genes modulate the relationship between plasma apoE and cortical PiB binding.Neurol Genet. 2015 Oct 15;1(3):e22. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000022. eCollection 2015 Oct. Neurol Genet. 2015. PMID: 27066559 Free PMC article.
-
The genetics and neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Sep;124(3):305-23. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0996-2. Epub 2012 May 23. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22618995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of Alzheimer's disease.Adv Genet. 2014;87:245-94. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800149-3.00005-6. Adv Genet. 2014. PMID: 25311924 Review.
Cited by
-
Different oral and gut microbial profiles in those with Alzheimer's disease consuming anti-inflammatory diets.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 15;9:974694. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.974694. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36185672 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiome Compositional and Functional Features Associate with Alzheimer's Disease Pathology.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 5:2024.09.04.24313004. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.04.24313004. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jul;21(7):e70417. doi: 10.1002/alz.70417. PMID: 39281749 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CD2AP at the junction of nephropathy and Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jun 4;20(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00852-x. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 40462155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Reprogramming in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders: A Review of Gut-Brain Communication and Emerging Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):11978. doi: 10.3390/ijms241511978. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease- and stage-specific alterations of the oral and fecal microbiota in Alzheimer's disease.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Dec 11;3(1):pgad427. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad427. eCollection 2024 Jan. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 38205031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeolu M., Alnajar S., Naushad S., Gupta R. S. (2016). Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66 5575–5599. 10.1099/ijsem.0.001485 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

