Yindan Jiedu Granules, a Traditional Chinese Medicinal Formulation, as a Potential Treatment for Coronavirus Disease 2019
- PMID: 33732148
- PMCID: PMC7957926
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.634266
Yindan Jiedu Granules, a Traditional Chinese Medicinal Formulation, as a Potential Treatment for Coronavirus Disease 2019
Abstract
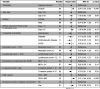
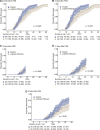
Background: Yindan Jiedu Granules (YDJDG) have been newly prescribed as a Chinese herbal formula. This study aimed to compare the efficacy of YDJDG and lopinavir-ritonavir in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Methods: Overall, 131 patients with COVID-19 were included in this study. In addition to standard care, 60 of these patients received YDJDG (YDJDG group) and 71 received lopinavir-ritonavir (lopinavir-ritonavir group). Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to match the characteristics of individuals in the two groups, while the Kaplan-Meier method was used to compare the proportion recovery observed. Results: Cox analysis revealed that YDJDG and CD4 ≥ 660 cells/µL were independent predictive factors of proportion recovery. At baseline, disease types differed between the YDJDG and lopinavir-ritonavir treatment groups. Furthermore, no significant adverse effects or toxicities relevant to YDJDG were observed. The median recovery time was 21 days in the YDJDG group and 27 days in the lopinavir-ritonavir group. After PSM (1:1), 50 patient pairs, YDJDG vs. lopinavir-ritonavir, were analyzed. In the YDJDG group, the proportion of recovered patients was remarkably higher than that observed in the lopinavir-ritonavir group (p = 0.0013), especially for those presenting mild/moderate disease type and CD4 < 660 cells/µL. In the YDJDG group, the mean duration of fever and pulmonary exudative lesions was significantly shorter than that observed in the lopinavir-ritonavir group (p = 0.0180 and p = 0.0028, respectively). Conclusion: YDJDG reveals the potential to hasten the recovery period in COVID-19 patients with mild/moderate disease type or CD4 < 660 cells/µL by shortening the mean duration of fever and pulmonary exudative lesions.
Keywords: COVID-19; Yindan Jiedu granules; fever; herbal medicine; pulmonary exudative lesions; recovery proportion.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Jiang, Liu, Pu, Du, Li, Wang, Ren, Liu, Yang, Chen, Song, Xie and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chan K. W., Wong V. T., Tang S. C. W. (2020). COVID-19: an update on the epidemiological, clinical, preventive and therapeutic evidence and guidelines of integrative Chinese-Western medicine for the management of 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 737–762. 10.1142/s0192415x20500378 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

