The Cranial Neural Crest in a Multiomics Era
- PMID: 33732166
- PMCID: PMC7956944
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.634440
The Cranial Neural Crest in a Multiomics Era
Abstract
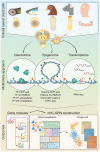
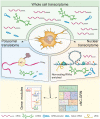
Neural crest ontogeny plays a prominent role in craniofacial development. In this Perspective article, we discuss recent advances to the understanding of mechanisms underlying the cranial neural crest gene regulatory network (cNC-GRN) stemming from omics-based studies. We briefly summarize how parallel considerations of transcriptome, interactome, and epigenome data significantly elaborated the roles of key players derived from pre-omics era studies. Furthermore, the growing cohort of cNC multiomics data revealed contribution of the non-coding genomic landscape. As technological improvements are constantly being developed, we reflect on key questions we are poised to address by taking advantage of the unique perspective a multiomics approach has to offer.
Keywords: epigenome; gene regulatory network; interactome; multiomics; neural crest; non-coding; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2021 Chong-Morrison and Sauka-Spengler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

