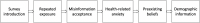An Examination of Factors Contributing to the Acceptance of Online Health Misinformation
- PMID: 33732192
- PMCID: PMC7957081
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.630268
An Examination of Factors Contributing to the Acceptance of Online Health Misinformation
Abstract
This study examined factors including health-related anxiety, preexisting misinformation beliefs, and repeated exposure contributing to individuals' acceptance of health misinformation. Through a large-scale online survey, this study found that health-related anxiety was positively associated with health misinformation acceptance. Preexisting misinformation beliefs, as well as repeated exposure to health misinformation, were both positively associated with health misinformation acceptance. The results also showed that demographic variables were significantly associated with health misinformation acceptance. In general, females accepted more health misinformation compared to males. Participants' age was negatively associated with health misinformation acceptance. Participants' education level and income were both negatively associated with their acceptance of health misinformation.
Keywords: health misinformation; health-related anxiety; misinformation acceptance; preexisting misinformation beliefs; repeated exposure; social media.
Copyright © 2021 Pan, Liu and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Brehmer B. (1976). Social judgment theory and the analysis of interpersonal conflict. Psychol. Bull. 83:985. 10.1037/0033-2909.83.6.985 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources