A New Method for Optimizing Sepsis Therapy by Nivolumab and Meropenem Combination: Importance of Early Intervention and CTL Reinvigoration Rate as a Response Marker
- PMID: 33732241
- PMCID: PMC7959825
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.616881
A New Method for Optimizing Sepsis Therapy by Nivolumab and Meropenem Combination: Importance of Early Intervention and CTL Reinvigoration Rate as a Response Marker
Abstract
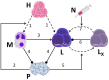
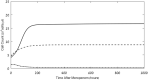
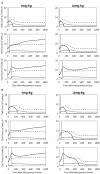
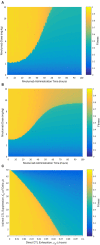
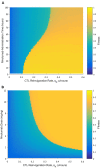
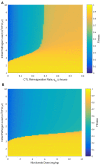
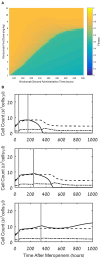
Background: Recently, there has been a growing interest in applying immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs), so far used to treat cancer, to patients with bacterial sepsis. We aimed to develop a method for predicting the personal benefit of potential treatments for sepsis, and to apply it to therapy by meropenem, an antibiotic drug, and nivolumab, a programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) pathway inhibitor. Methods: We defined an optimization problem as a concise framework of treatment aims and formulated a fitness function for grading sepsis treatments according to their success in accomplishing the pre-defined aims. We developed a mathematical model for the interactions between the pathogen, the cellular immune system and the drugs, whose simulations under diverse combined meropenem and nivolumab schedules, and calculation of the fitness function for each schedule served to plot the fitness landscapes for each set of treatments and personal patient parameters. Results: Results show that treatment by meropenem and nivolumab has maximum benefit if the interval between the onset of the two drugs does not exceed a dose-dependent threshold, beyond which the benefit drops sharply. However, a second nivolumab application, within 7-10 days after the first, can extinguish a pathogen which the first nivolumab application failed to remove. The utility of increasing nivolumab total dose above 6 mg/kg is contingent on the patient's personal immune attributes, notably, the reinvigoration rate of exhausted CTLs and the overall suppression rates of functional CTLs. A baseline pathogen load, higher than 5,000 CFU/μL, precludes successful nivolumab and meropenem combination therapy, whereas when the initial load is lower than 3,000 CFU/μL, meropenem monotherapy suffices for removing the pathogen. Discussion: Our study shows that early administration of nivolumab, 6 mg/kg, in combination with antibiotics, can alleviate bacterial sepsis in cases where antibiotics alone are insufficient and the initial pathogen load is not too high. The study pinpoints the role of precision medicine in sepsis, suggesting that personalized therapy by ICBs can improve pathogen elimination and dampen immunosuppression. Our results highlight the importance in using reliable markers for classifying patients according to their predicted response and provides a valuable tool in personalizing the drug regimens for patients with sepsis.
Keywords: PD-1; fitness landscape; immunosuppression; inflammation; intensive care; mathematical model; nivolumab; simulation.
Copyright © 2021 Gillis, Ben Yaacov and Agur.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint inhibition in sepsis: a Phase 1b randomized study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of nivolumab.Intensive Care Med. 2019 Oct;45(10):1360-1371. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05704-z. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Intensive Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31576433 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Can Reduce HCV-RNA without Liver Damage.Intern Med. 2020 Sep 15;59(18):2245-2248. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3726-19. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32522918 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation of exhaustion-induced immunosuppression and sepsis by immune checkpoint blockers sequentially administered with antibiotics-analysis of a new mathematical model.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019 Jun 11;7(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40635-019-0260-3. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2019. PMID: 31187301 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Development of Immunotherapy for Deficient Mismatch Repair Colorectal Cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2020 Jun;19(2):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32173280 Review.
-
Nivolumab and its use in the second-line treatment of metastatic urothelial cancer.Future Oncol. 2018 Nov;14(26):2683-2690. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0735. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29927336 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical management of sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: current evidence and future directions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 26;12:1531275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1531275. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40491760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Monoclonal Antibody-Based Approaches in the Management of Bacterial Sepsis.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 2;11(3):765. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030765. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current perspectives in the management of sepsis and septic shock.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 15;11:1431791. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1431791. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39211340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The implication of targeting PD-1:PD-L1 pathway in treating sepsis through immunostimulatory and anti-inflammatory pathways.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 13;14:1323797. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1323797. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38193090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gomez JL, Himes BE, Kaminski N. Precision in Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine. A clinical and Research Guide. 1st ed. Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Humana Press; (2020). 10.1007/978-3-030-31507-8 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

