The Dynamic Immune Response of Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Infected With Edwardsiella ictaluri Presenting the Inflammation Process
- PMID: 33732247
- PMCID: PMC7959794
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.625928
The Dynamic Immune Response of Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Infected With Edwardsiella ictaluri Presenting the Inflammation Process
Abstract
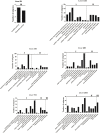
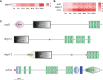
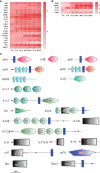
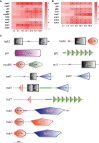
Edwardsiella ictaluri is a highly destructive pathogen in cultured yellow catfish, thus it was very necessary to study the immune response of yellow catfish against bacterial infection. In this study, RNA-Seq technology was used to study the immune response in two distinct tissues of yellow catfish at eight different time points (h) after E. ictaluri infection. The number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the spleen and liver was low at 3 h and 6 h post-infection, respectively. Afterwards, the most number of DEGs in the spleen was detected at 72 h, while the number of DEGs in the liver maintained a high level from 24 h to 120 h. The GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of DEGs at different time points uncovered that cytokines were continuously transcribed at 6 h to 120 h; whereas the liver is the main organ that secretes the components of the complement system, and metabolic regulation was activated from 12 h to 120 h. Moreover, an overview of the inflammation response of yellow catfish was exhibited including pattern-recognition receptors, inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, complements, and inflammation-related signal pathways. The similar expression tendency of nine genes by qRT-PCR validated the accuracy of transcriptome analyses. The different transcriptomic profiles obtained from the spleen and liver will help to better understand the dynamic immune response of fish against bacterial infection, and will provide basic information for establishing effective measures to prevent and control diseases in fish.
Keywords: Edwardsiella ictaluri; bacteria; inflammation; transcriptome; yellow catfish.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Zhang, Ji, Shi, Ma, Luo and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The RAG2 gene of yellow catfish (Tachysurus fulvidraco) and its immune response against Edwardsiella ictaluri infection.Dev Comp Immunol. 2019 Sep;98:65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Dev Comp Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31002844
-
Deciphering transcriptome profile of the yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) in response to Edwardsiella ictaluri.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Nov;70:593-608. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.08.040. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28866276
-
Hematological and immune genes responses in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) with septicemia induced by Edwardsiella ictaluri.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020 Feb;97:531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.11.071. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31794844
-
Molecular cloning and expression analysis of interleukin-1β and interleukin-1 receptor type I genes in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco): Responses to challenge of Edwardsiella ictaluri.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Sep;223:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 22. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29775651
-
Molecular Characterization of Nine TRAF Genes in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) and Their Expression Profiling in Response to Edwardsiella ictaluri Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 6;24(9):8363. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098363. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176078 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Molecular Immunopathogenesis of Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Trionyx sinensis) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila.Biology (Basel). 2021 Nov 22;10(11):1218. doi: 10.3390/biology10111218. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827211 Free PMC article.
-
Applying genetic technologies to combat infectious diseases in aquaculture.Rev Aquac. 2023 Mar;15(2):491-535. doi: 10.1111/raq.12733. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Rev Aquac. 2023. PMID: 38504717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Attenuation Mechanism and Live Vaccine Potential of a Low-Virulence Edwardsiella ictaluri Strain Obtained by Rifampicin Passaging Culture.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 28;33(2):167-179. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2210.10013. Epub 2022 Dec 9. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36734130 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Sequencing Analysis of the Spleen and Gill of Takifugu rubripes in Response to Vibrio harveyi Infection.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jan 31;8:813988. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.813988. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35174239 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed genes in head kidney of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco following Vibrio cholerae challenge.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1039956. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1039956. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36703962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gao C, Fu Q, Su B, Zhou S, Liu F, Song L, et al. . Transcriptomic profiling revealed the signatures of intestinal barrier alteration and pathogen entry in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) following Vibrio anguillarum challenge. Dev Comp Immunol (2016) 65:159–68. 10.1016/j.dci.2016.07.007 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

