4-Hexylresorcinol inhibits osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and reverses bone loss in ovariectomized mice
- PMID: 33732327
- PMCID: PMC7903454
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9785
4-Hexylresorcinol inhibits osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and reverses bone loss in ovariectomized mice
Abstract
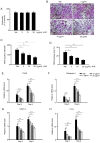
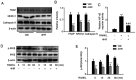
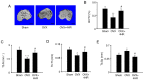
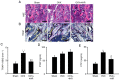
4-Hexylresorcinol (4HR) is a small organic compound that is widely used as an antiseptic and antioxidant. In the present study, its role in osteoclastogenesis was investigated. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from mice were used to examine the role of 4HR in osteogenesis. An ovariectomy (OVX) mouse model was constructed to examine the effect of 4HR in vivo, followed by hematoxylin and eosin and tartrate resistant acid phosphatase staining. In the present study, 4HR effectively suppressed receptor activator of NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. 4HR was also found to significantly suppress the expression of osteoclast (OC)-specific markers, including tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, cathepsin K, nuclear factor of activated T-cell cytoplasmic 1 and c-Fos in the presence of RANKL in BMMs. Furthermore, 4HR inhibited osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in BMMs. Consistent with the in vitro results, 4HR effectively ameliorated OVX-induced bone loss and markedly reduced OC number in the proximal tibia in vivo. In conclusion, the present results suggested that 4HR inhibited osteoclastogenesis in vitro and rescued bone loss in vivo, suggesting that 4HR may serve as a novel therapeutic agent for osteoporosis treatment.
Keywords: 4-Hexylresorcinol; osteoclast; osteoclastogenesis; ovariectomy.
Copyright: © Yi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
4-Hexylresorcinol: pharmacologic chaperone and its application for wound healing.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Feb 1;44(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40902-022-00334-w. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022. PMID: 35103875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand–induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase/activator protein 1 and Ca2+–nuclear factor of activated T-cells cytoplasmic 1 signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Jun;27(6):1298-1308. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1576. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22337253
-
Pseurotin A Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Bone Loss by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species.Theranostics. 2019 Feb 28;9(6):1634-1650. doi: 10.7150/thno.30206. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31037128 Free PMC article.
-
Neogambogic Acid Suppresses Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor κB Ligand (RANKL)-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Inhibiting the JNK and NF-κB Pathways in Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Monocyte/Macrophages.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Apr 26;24:2569-2577. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909651. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29698379 Free PMC article.
-
Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Bone. 2015 Jun;75:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Bone. 2015. PMID: 25708053
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of 4-Hexylresorcinol in Preserving Testicular Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 13;25(8):4316. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084316. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673900 Free PMC article.
-
4-Hexylresorcinol: pharmacologic chaperone and its application for wound healing.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Feb 1;44(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40902-022-00334-w. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022. PMID: 35103875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergård M, Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jönsson B, Kanis JA. Osteoporosis in the European union: Medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the international osteoporosis foundation (IOF) and the European federation of pharmaceutical industry associations (EFPIA) Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8(136) doi: 10.1007/s11657-013-0136-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tom SE, Adachi JD, Anderson FA Jr, Boonen S, Chapurlat RD, Compston JE, Cooper C, Gehlbach SH, Greenspan SL, Hooven FH, et al. Frailty and fracture, disability, and falls: A multiple country study from the global longitudinal study of osteoporosis in women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013;61:327–334. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12146. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
