Complete lung collapse as a rare complication of sarcoidosis-associated mediastinal lymphadenopathy
- PMID: 33732471
- PMCID: PMC7946853
- DOI: 10.1002/rcr2.739
Complete lung collapse as a rare complication of sarcoidosis-associated mediastinal lymphadenopathy
Abstract
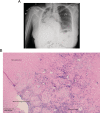
Complete lung collapse associated with sarcoidosis is exceedingly rare. Although lymphoma should be ruled out when patients with mediastinal lymphadenopathy develop lung collapse, sarcoidosis should be considered in the differential, especially when associated with fibrosing mediastinitis.
Keywords: Atelectasis; fibrosing mediastinitis; lymphadenopathy; lymphoma; sarcoidosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Respirology Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of The Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Figures
References
-
- Fender EA, Widmer RJ, Knavel Koepsel EM, et al. 2019. Catheter based treatments for fibrosing mediastinitis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 94(6):878–885. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

