Knowledge Models as Teaching Aid for Training Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Planning: A Lung Cancer Case Study
- PMID: 33733183
- PMCID: PMC7861316
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2020.00066
Knowledge Models as Teaching Aid for Training Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy Planning: A Lung Cancer Case Study
Abstract
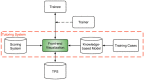
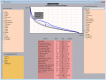
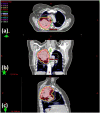
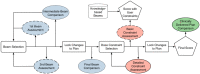
Purpose: Artificial intelligence (AI) employs knowledge models that often behave as a black-box to the majority of users and are not designed to improve the skill level of users. In this study, we aim to demonstrate the feasibility that AI can serve as an effective teaching aid to train individuals to develop optimal intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plans. Methods and Materials: The training program is composed of a host of training cases and a tutoring system that consists of a front-end visualization module powered by knowledge models and a scoring system. The current tutoring system includes a beam angle prediction model and a dose-volume histogram (DVH) prediction model. The scoring system consists of physician chosen criteria for clinical plan evaluation as well as specially designed criteria for learning guidance. The training program includes six lung/mediastinum IMRT patients: one benchmark case and five training cases. A plan for the benchmark case is completed by each trainee entirely independently pre- and post-training. Five training cases cover a wide spectrum of complexity from easy (2), intermediate (1) to hard (2). Five trainees completed the training program with the help of one trainer. Plans designed by the trainees were evaluated by both the scoring system and a radiation oncologist to quantify planning quality. Results: For the benchmark case, trainees scored an average of 21.6% of the total max points pre-training and improved to an average of 51.8% post-training. In comparison, the benchmark case's clinical plans score an average of 54.1% of the total max points. Two of the five trainees' post-training plans on the benchmark case were rated as comparable to the clinically delivered plans by the physician and all five were noticeably improved by the physician's standards. The total training time for each trainee ranged between 9 and 12 h. Conclusion: This first attempt at a knowledge model based training program brought unexperienced planners to a level close to experienced planners in fewer than 2 days. The proposed tutoring system can serve as an important component in an AI ecosystem that will enable clinical practitioners to effectively and confidently use KBP.
Keywords: intensity modulated radiation therapy; knowledge model; lung cancer; machine learning; tutoring system.
Copyright © 2020 Mistro, Sheng, Ge, Kelsey, Palta, Cai, Wu, Yin and Wu.
Figures
References
-
- Chapet O., Kong F.-M., Lee J. S., Hayman J. A., Ten Haken R. K. (2005). Normal tissue complication probability modeling for acute esophagitis in patients treated with conformal radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 77, 176–181. 10.1016/j.radonc.2005.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chun S. G., Hu C., Choy H., Komaki R. U., Timmerman R. D., Schild S. E., et al. (2017). Impact of intensity-modulated radiation therapy technique for locally advanced non–small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the NRG oncology RTOG 0617 randomized clinical trial. Clin. Trial 35, 56–62. 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.1378 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dermeval D., Paiva R., Bittencourt I. I., Vassileva J., Borges D. (2018). Authoring tools for designing intelligent tutoring systems: a systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Artificial Intelligence Edu. 28, 336–384. 10.1007/s40593-017-0157-9 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

