RNA and DNA G-quadruplexes bind to human dicer and inhibit its activity
- PMID: 33733306
- PMCID: PMC8038994
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03795-w
RNA and DNA G-quadruplexes bind to human dicer and inhibit its activity
Abstract
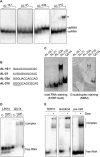
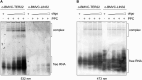
Guanine (G)-rich single-stranded nucleic acids can adopt G-quadruplex structures. Accumulating evidence indicates that G-quadruplexes serve important regulatory roles in fundamental biological processes such as DNA replication, transcription, and translation, while aberrant G-quadruplex formation is linked to genome instability and cancer. Understanding the biological functions played by G-quadruplexes requires detailed knowledge of their protein interactome. Here, we report that both RNA and DNA G-quadruplexes are bound by human Dicer in vitro. Using in vitro binding assays, mutation studies, and computational modeling we demonstrate that G-quadruplexes can interact with the Platform-PAZ-Connector helix cassette of Dicer, the region responsible for anchoring microRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs). Consequently, we show that G-quadruplexes efficiently and stably inhibit the cleavage of pre-miRNA by Dicer. Our data highlight the potential of human Dicer for binding of G-quadruplexes and allow us to propose a G-quadruplex-driven sequestration mechanism of Dicer regulation.
Keywords: Dicer PPC cassette; Dicer inhibition; MiRNA biogenesis; PAZ domain; Regulation of enzyme activity; Ribonucleoprotein complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

