Pharmacometrics-Based Considerations for the Design of a Pharmacogenomic Clinical Trial Assessing Irinotecan Safety
- PMID: 33733372
- PMCID: PMC8057977
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-021-03024-w
Pharmacometrics-Based Considerations for the Design of a Pharmacogenomic Clinical Trial Assessing Irinotecan Safety
Abstract
Purpose: Pharmacometric models provide useful tools to aid the rational design of clinical trials. This study evaluates study design-, drug-, and patient-related features as well as analysis methods for their influence on the power to demonstrate a benefit of pharmacogenomics (PGx)-based dosing regarding myelotoxicity.
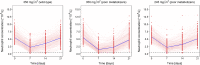
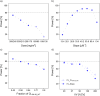
Methods: Two pharmacokinetic and one myelosuppression model were assembled to predict concentrations of irinotecan and its metabolite SN-38 given different UGT1A1 genotypes (poor metabolizers: CLSN-38: -36%) and neutropenia following conventional versus PGx-based dosing (350 versus 245 mg/m2 (-30%)). Study power was assessed given diverse scenarios (n = 50-400 patients/arm, parallel/crossover, varying magnitude of CLSN-38, exposure-response relationship, inter-individual variability) and using model-based data analysis versus conventional statistical testing.
Results: The magnitude of CLSN-38 reduction in poor metabolizers and the myelosuppressive potency of SN-38 markedly influenced the power to show a difference in grade 4 neutropenia (<0.5·109 cells/L) after PGx-based versus standard dosing. To achieve >80% power with traditional statistical analysis (χ2/McNemar's test, α = 0.05), 220/100 patients per treatment arm/sequence (parallel/crossover study) were required. The model-based analysis resulted in considerably smaller total sample sizes (n = 100/15 given parallel/crossover design) to obtain the same statistical power.
Conclusions: The presented findings may help to avoid unfeasible trials and to rationalize the design of pharmacogenetic studies.
Keywords: UGT1A1; irinotecan model; neutropenia; pharmacogenomics; study design.
Figures




References
-
- Lauschke VM, Milani L, Ingelman-Sundberg M. Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers for Improved Drug Therapy—Recent Progress and Future Developments. AAPS J. 2017;20(1). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

