Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Oxazolo[3,4- a]pyrazine Derivatives Leading to the Discovery of a Novel Neuropeptide S Receptor Antagonist with Potent In Vivo Activity
- PMID: 33733768
- PMCID: PMC8041306
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02223
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies on Oxazolo[3,4- a]pyrazine Derivatives Leading to the Discovery of a Novel Neuropeptide S Receptor Antagonist with Potent In Vivo Activity
Abstract
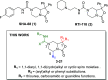
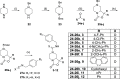
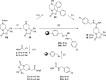
Neuropeptide S modulates important neurobiological functions including locomotion, anxiety, and drug abuse through interaction with its G protein-coupled receptor known as neuropeptide S receptor (NPSR). NPSR antagonists are potentially useful for the treatment of substance abuse disorders against which there is an urgent need for new effective therapeutic approaches. Potent NPSR antagonists in vitro have been discovered which, however, require further optimization of their in vivo pharmacological profile. This work describes a new series of NPSR antagonists of the oxazolo[3,4-a]pyrazine class. The guanidine derivative 16 exhibited nanomolar activity in vitro and 5-fold improved potency in vivo compared to SHA-68, a reference pharmacological tool in this field. Compound 16 can be considered a new tool for research studies on the translational potential of the NPSergic system. An in-depth molecular modeling investigation was also performed to gain new insights into the observed structure-activity relationships and provide an updated model of ligand/NPSR interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



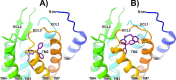
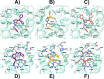

References
-
- Syuji S.; Yasushi S.; Nobuyuki M.; Koji Y.. cDNA and protein sequence of a novel human and animal G protein-coupled receptors and their uses in drug screening, diagnosis, and therapeutics. WO2002031145A1, April 18, 2002.
-
- Xu Y.-L.; Reinscheid R. K.; Huitron-Resendiz S.; Clark S. D.; Wang Z.; Lin S. H.; Brucher F. A.; Zeng J.; Ly N. K.; Henriksen S. J.; de Lecea L.; Civelli O. Neuropeptide S: a neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects. Neuron 2004, 43, 487–497. 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

