Blinatumomab as first salvage versus second or later salvage in adults with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of a pooled analysis
- PMID: 33734596
- PMCID: PMC8026950
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3731
Blinatumomab as first salvage versus second or later salvage in adults with relapsed/refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of a pooled analysis
Abstract
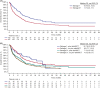
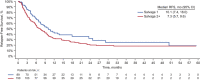
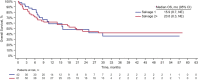
Blinatumomab is a BiTE® immuno-oncology therapy indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory (r/r) B-cell precursor (BCP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Aims To assess the efficacy and safety of blinatumomab as first salvage versus second or later salvage in patients with r/r BCP ALL. Materials & Methods Patient-level pooled data were used for this analysis. In total, 532 adults with r/r BCP ALL treated with blinatumomab were included (first salvage, n = 165; second or later salvage, n = 367). Results Compared with patients who received blinatumomab as second or later salvage, those who received blinatumomab as first salvage had a longer median overall survival (OS; 10.4 vs. 5.7 months; HR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.26-1.97; P < .001) and relapse-free survival (10.1 vs. 7.3 months; HR, 1.38; 95% CI, 0.98-1.93; P = .061), and higher rates of remission (n = 89 [54%] vs. n = 150 [41%]; odds ratio, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.41-0.85; P = .005), minimal residual disease response (n = 68 [41%] vs. n = 118 [32%]), and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloHSCT) realization (n = 60 [36%] vs. n = 88 [24%]), and alloHSCT in continuous remission (n = 33 [20%] vs. n = 52 (14%]). In a subgroup analysis, there was no apparent effect of prior alloHSCT on median OS in either salvage group. The safety profile of blinatumomab was generally similar between the groups; however, cytokine release syndrome, febrile neutropenia, and infection were more frequent with second or later salvage than with first salvage. Discussion In this pooled analysis, the logistic regression analyses indicated greater benefit with blinatumomab as first salvage than as second or later salvage, as evident by the longer median OS, longer median RFS, and higher rates of remission. Conclusion Overall, blinatumomab was beneficial as first salvage and as second or later salvage, but the effects were favorable as first salvage.
Keywords: BiTE®; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; blinatumomab; salvage; stem cell transplant.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Max S. Topp: received fees for serving on the advisory boards of Amgen Inc., Regeneron, Affimed, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Gilead Sciences, and Pfizer, and travel support from Amgen Inc., Roche, Regeneron, and Affimed.
Anthony S. Stein: participated in speakers’ bureau for Amgen Inc., Celgene, and Stemline.
Nicola Gökbuget: served on the advisory board and speakers’ bureau of, and received research funding from Amgen Inc.; served on the advisory board and speakers’ bureau of, and received travel support from Pfizer.
Heinz‐August Horst: received research funding, travel support from, and participated in advisory boards for Amgen Inc.; participated in advisory board for Pfizer, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis; and received research funding from Regeneron.
Nicolas Boissel: provides consultancy to Amgen Inc.
Giovanni Martinelli: no disclosures.
Hagop Kantarjian: received research funding from AbbVie, Agios, Amgen Inc., Ariad, Astex, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Cyclacel, Daiichi‐Sankyo, ImmunoGen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer; and received honoraria from AbbVie, Actinium, Agios, Amgen Inc., Pfizer, and Takeda.
Monika Brüggemann: received consulting fees and honoraria from Amgen Inc., Celgene, Incyte, Janssen, and Roche, and research funding from Affimed, Regeneron, and Roche.
Yuqi Chen is an employee of and owns stock in Amgen Inc.
Gerhard Zugmaier is an employee of, has patents from, and owns stock in Amgen Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Dreier T, Lorenczewski G, Brandl C, et al. Extremely potent, rapid and costimulation‐independent cytotoxic T‐cell response against lymphoma cells catalyzed by a single‐chain bispecific antibody. Int J Cancer. 2002;100:690‐697. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann P, Hofmeister R, Brischwein K, et al. Serial killing of tumor cells by cytotoxic T cells redirected with a CD19‐/CD3‐bispecific single‐chain antibody construct. Int J Cancer. 2005;115:98‐104. - PubMed
-
- Loffler A, Gruen M, Wuchter C, et al. Efficient elimination of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia B cells by autologous T cells with a bispecific anti‐CD19/anti‐CD3 single‐chain antibody construct. Leukemia. 2003;17:900‐909. - PubMed
-
- Topp MS, Gokbuget N, Stein AS, et al. Safety and activity of blinatumomab for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B‐precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a multicentre, single‐arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:57‐66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

