Adverse childhood experiences, racial microaggressions, and alcohol misuse in Black and White emerging adults
- PMID: 33734786
- PMCID: PMC8084861
- DOI: 10.1037/adb0000597
Adverse childhood experiences, racial microaggressions, and alcohol misuse in Black and White emerging adults
Abstract
Objective: Research indicates that emerging adults (EAs) are at an increased risk for heavy drinking and its associated alcohol problems, and that both proximal and distal stressors (e.g., adverse childhood experiences [ACEs], and subtle racial discrimination [racial microaggressions]) may contribute to these high-risk outcomes. We investigated the relationship of ACEs with alcohol consumption and alcohol problems in a sample of Black and White EAs, and racial microaggressions with alcohol consumption and alcohol problems in the Black EAs in our sample.
Method: Six hundred two EAs (41.5% Black, 47% White; 57.3% women) completed measures assessing ACEs, alcohol consumption, and alcohol problems. One hundred ninety-six Black EAs in the sample were also asked to complete a measure of racial microaggressions that assessed their level of distress related to these experiences.
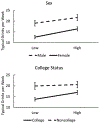
Results: Regression analyses demonstrated a positive association of ACEs with alcohol consumption and alcohol problems. Sex moderated the relation of ACEs with alcohol consumption such that the positive relationship between ACEs and alcohol consumption was minimally stronger for females. College status moderated the relation of ACEs with alcohol consumption such that the relationship between ACEs and alcohol consumption was stronger for college students than non-college students. Racial microaggressions were positively associated with alcohol problems, but not alcohol consumption.
Conclusion: Findings underscore the importance of childhood stressors with alcohol consumption and problems for EAs, and the need for additional research on racial microaggressions and alcohol problems in Black EAs. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2021 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
References
-
- Aiken LS, & West SG (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage Publications, Inc.
-
- Aneshensel CS (1992). Social stress theory and research. Annual Review of Sociology, 18, 15–38. Retrieved from http://10.0.4.122/annurev.so.18.080192.000311 - DOI
-
- American Psychological Association, APA Working Group on Stress and Health Disparities.(2017). Stress and health disparities: Contexts, mechanisms, and interventions among racial/ethnic minority and low-socioeconomic status populations. Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/pi/health-disparities/resources/stress-report.aspx
-
- Armeli S, Tennen H, Todd M, Carney MA, Mohr C, Affleck G, & Hromi A (2003). A daily process examination of the stress-response dampening effects of alcohol consumption. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 17(4), 266–276. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources