Imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in typical and atypical sites: Long term follow up
- PMID: 33735214
- PMCID: PMC7971862
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248589
Imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma in typical and atypical sites: Long term follow up
Abstract
Purpose: To assess efficacy and safety of imaging-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of Osteoid Osteoma (OO) in both typical and atypical sites.
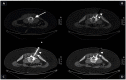
Methods and materials: Between January 2014 and March 2019, 102 consecutive percutaneous RFA were performed and retrospectively reviewed. The procedures were performed using a RFA bipolar ablation system (Covidien, exposed tip of 0.7-1cm), under Computed Tomography (CT) guidance or using a navigation system (Masmec) under CT and Cone Beam CT (CBCT) guidance. Patients were followed up over 24 months. Clinical success and recurrences were considered on the base of established criteria. In patients with clinical failure and/or imaging evidence of relapse, retreatment was considered.
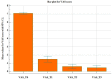
Results: Administered power per-procedure was ≤8 W (mean temperature, 90°C). The pre-procedure average value of visual analog scale (VAS) was 8.33+/-0.91. Primary and secondary success rate 96.08% (98/102) and100% (102/102), respectively. No major complication was described. Technical success was proved in every patient by CT scan acquisition after needle positioning. Relapse and tumour location were significantly correlated (p-value = 0.0165). The mean dose-length product was 751.55 mGycm2. Advanced bone healing was noted in 68 lesions after 1y-follow up and in 86 lesions after 2y-follow up.
Conclusion: Imaging-guided percutaneous RFA is a highly effective technique for OO, both in typical and atypical sites. CT or CBCT guidance, navigation systems and operator experience grant the technical success, which is the most crucial parameter affecting outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) guidance is helpful in reducing dose exposure to pediatric patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma.Radiol Med. 2022 Feb;127(2):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01439-4. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 34958441 Free PMC article.
-
Computed Tomography-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Osteoid Osteoma in Atypical Sites: Efficacy and Safety in a Large Case Series.Acad Radiol. 2021 Jan;28(1):68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.01.028. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Acad Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32111469
-
Atypically Located Osteoid Osteoma: Characteristics and Therapeutic Success After Image-Guided Thermal Ablation.Rofo. 2020 Apr;192(4):335-342. doi: 10.1055/a-1012-2143. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Rofo. 2020. PMID: 31747706 English, German.
-
Percutaneous thermal ablation for treatment of osteoid osteoma: a systematic review and analysis.Skeletal Radiol. 2020 Sep;49(9):1403-1411. doi: 10.1007/s00256-020-03435-7. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Skeletal Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32270226
-
[Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteomas: technique and results].Rofo. 2009 Aug;181(8):740-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109424. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Rofo. 2009. PMID: 19517335 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Global research progress on radiofrequency ablation in cardiology: A bibliometric analysis (2004-2023).Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 7;103(23):e38498. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038498. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38847657 Free PMC article.
-
The surgical management of osteoid osteoma: A systematic review.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 22;12:935640. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.935640. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35936708 Free PMC article.
-
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) guidance is helpful in reducing dose exposure to pediatric patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma.Radiol Med. 2022 Feb;127(2):183-190. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01439-4. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 34958441 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and Long-Term Outcomes after Radiofrequency Ablation of Osteoid Osteomas.J Pers Med. 2024 Apr 10;14(4):401. doi: 10.3390/jpm14040401. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38673028 Free PMC article.
-
CT-Guided Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation for the Treatment of Atypical, Early-Onset Osteoid Osteoma in Children Younger than 4 Years Old: Single-Institution Experience and Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;12(11):2812. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112812. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428872 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

