Assembly assay identifies a critical region of human fibrillin-1 required for 10-12 nm diameter microfibril biogenesis
- PMID: 33735269
- PMCID: PMC7971562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248532
Assembly assay identifies a critical region of human fibrillin-1 required for 10-12 nm diameter microfibril biogenesis
Abstract
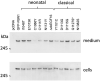
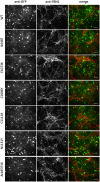
The human FBN1 gene encodes fibrillin-1 (FBN1); the main component of the 10-12 nm diameter extracellular matrix microfibrils. Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a common inherited connective tissue disorder, caused by FBN1 mutations. It features a wide spectrum of disease severity, from mild cases to the lethal neonatal form (nMFS), that is yet to be explained at the molecular level. Mutations associated with nMFS generally affect a region of FBN1 between domains TB3-cbEGF18-the "neonatal region". To gain insight into the process of fibril assembly and increase our understanding of the mechanisms determining disease severity in MFS, we compared the secretion and assembly properties of FBN1 variants containing nMFS-associated substitutions with variants associated with milder, classical MFS (cMFS). In the majority of cases, both nMFS- and cMFS-associated neonatal region variants were secreted at levels comparable to wild type. Microfibril incorporation by the nMFS variants was greatly reduced or absent compared to the cMFS forms, however, suggesting that nMFS substitutions disrupt a previously undefined site of microfibril assembly. Additional analysis of a domain deletion variant caused by exon skipping also indicates that register in the neonatal region is likely to be critical for assembly. These data demonstrate for the first time new requirements for microfibril biogenesis and identify at least two distinct molecular mechanisms associated with disease substitutions in the TB3-cbEGF18 region; incorporation of mutant FBN1 into microfibrils changing their integral properties (cMFS) or the blocking of wild type FBN1 assembly by mutant molecules that prevents late-stage lateral assembly (nMFS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel fibrillin-1 gene missense mutation associated with neonatal Marfan syndrome: a case report and review of the mutation spectrum.BMC Pediatr. 2016 Apr 30;16:60. doi: 10.1186/s12887-016-0598-6. BMC Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27138491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A microfibril assembly assay identifies different mechanisms of dominance underlying Marfan syndrome, stiff skin syndrome and acromelic dysplasias.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Aug 1;24(15):4454-63. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv181. Epub 2015 May 15. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25979247 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the structure, assembly and biological roles of 10-12 nm connective tissue microfibrils from fibrillin-1 studies.Biochem J. 2016 Apr 1;473(7):827-38. doi: 10.1042/BJ20151108. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27026396 Review.
-
Steered molecular dynamic simulations reveal Marfan syndrome mutations disrupt fibrillin-1 cbEGF domain mechanosensitive calcium binding.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 8;10(1):16844. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73969-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33033378 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo studies of mutant fibrillin-1 microfibrils.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 6;285(32):24943-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130021. Epub 2010 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20529844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic analysis of a novel FBN1 mutation in a pediatric Marfan syndrome patient.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2024 Aug 31;13(3):178-184. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2024.01029. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2024. PMID: 39220279 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial dysfunction in Marfan syndrome mice is restored by resveratrol.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 28;12(1):22504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26662-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36577770 Free PMC article.
-
Marfan syndrome variation of the POGLUT2 and POGLUT3 consensus sequence can produce aberrant fibrillin-1 O-glucosylation.J Biol Chem. 2025 May;301(5):108411. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108411. Epub 2025 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40107616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jovanovic J, Takagi J, Choulier L, Abrescia NG, Stuart DI, van der Merwe PA, et al.. alphaVbeta6 is a novel receptor for human fibrillin-1. Comparative studies of molecular determinants underlying integrin-rgd affinity and specificity. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2007;282(9):6743–51. 10.1074/jbc.M607008200 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

