Phase 1b trial of isatuximab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, in combination with carfilzomib as treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
- PMID: 33735504
- PMCID: PMC8252002
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.33448
Phase 1b trial of isatuximab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, in combination with carfilzomib as treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
Abstract
Background: Isatuximab (Isa), an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, and carfilzomib (K), a next-generation proteasome inhibitor (PI), both have potent single-agent activity in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM).
Methods: This phase 1b study evaluated the combination of Isa and K in 33 patients with RRMM. Isa was administered by intravenous infusion in 3 dosing cohorts: dose level 1 (Isa at 10 mg/kg biweekly), dose level 2 (DL2; Isa at 10 mg/kg weekly for 4 doses and then biweekly), and dose level 3 (Isa at 20 mg/kg weekly for 4 doses and then biweekly) and all patients received K (20 mg/m2 intravenously for cycle 1, days 1 and 2, and then 27 mg/m2 for all subsequent doses). A standard 3+3 dose-escalation design was used, no dose-limiting toxicity was observed, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached. An expansion cohort of 18 patients was enrolled at DL2 to further evaluate safety and efficacy. Responses were assessed with the International Myeloma Working Group response criteria, and patients continued treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
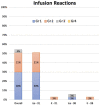
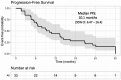
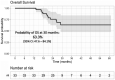
Results: With a median follow-up of 26.7 months, in this heavily pretreated population with a median of 3 prior lines (refractory to PIs and immunomodulatory drugs, 76%; refractory to K, 27%), the overall response rate was 70% (stringent complete response/complete response, 4; very good partial response, 8; partial response, 11). The median progression-free survival was 10.1 months, and the 2-year survival probability was 76%. The most common treatment-related adverse events (grade 2 or higher) were anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hypertension, and infection. Infusion reactions were common (55%) but did not limit dosing.
Conclusions: Treatment with Isa plus K was well tolerated with no unexpected toxicity. The combination was effective despite the enrollment of heavily pretreated patients with RRMM.
Lay summary: This phase 1b study was designed to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of isatuximab and carfilzomib in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Thirty-three patients were treated: 15 in dose escalation and 18 in dose expansion. Patients received an average of 10 cycles. The treatment was safe and effective. No unexpected toxicity or drug-drug interactions were noted. Seventy percent of the subjects responded to therapy, and the progression-free survival was 10.1 months.
Keywords: carfilzomib; immunomodulatory; isatuximab; monoclonal antibody; pharmacokinetics; proteasome.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Thomas G. Martin reports research funding (institutional) from Sanofi, Amgen, Janssen, and Seattle Genetics and consultancy for Roche and GlaxoSmithKline. Nina Shah reports research funding (institutional) from Bluebird Bio, Janssen, Celgene/Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Sutro Biopharma, TeneoBio, Poseida, and Nektar and consultancy for and honoraria from Celgene, Janssen, Bluebird Bio, Sutro Biopharma, Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Oncopeptides, Karyopharm, Surface Oncology, Precision Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Nektar, Amgen, Indapta Therapeutics, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, CareDx, Kite, Karyopharm, and Sanofi. Joshua Richter reports consultancy and membership on an advisory board for Sanofi. David H. Vesole reports research funding (institutional) from Sanofi and Amgen; stock and other ownership interests in Amgen, AbbVie, Biogen, Celgene/Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Johnson & Johnson, Lilly, and Novartis; honoraria from or consultancy for Amgen, Takeda, Celgene, and Pfizer; and membership in speakers’ bureaus for Amgen, Celgene/Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Janssen Oncology, GlaxoSmithKline, and Takeda. Sandy W. Wong reports research funding (institutional) from Bristol‐Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Roche/Genentech, and Fortis and consultancy or membership on an advisory committee for Amgen and Sanofi. Deepu Madduri reports research funding (institutional) from Janssen and Regeneron; membership in speakers’ bureaus for Shire, Legend, Kinevant, and GlaxoSmithKline; honoraria from Janssen, Celgene, and AbbVie; and consultancy for Foundation Medicine and Takeda. Sundar Jagannath reports consultancy for Legend Biotech, Takeda, AbbVie, Celgene, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, Janssen, and Merck and membership on scientific advisory boards for Celgene, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, and Sanofi‐Aventis. David S. Siegel reports research funding (institutional) from Celgene; stock and other ownership interests in Cellularity; consulting or advisory roles with Amgen, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen Oncology, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Karyopharm Therapeutics, and Merck; and membership in speakers’ bureaus for Amgen, Celgene, Takeda, Janssen Oncology, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb. Noa Biran reports research funding (institutional) from Merck, Karyopharm Therapeutics, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb; honoraria from or consultancy for Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Amgen, Celgene, Takeda, and Janssen Oncology; and membership in speakers’ bureaus for Takeda, Celgene, Amgen, Janssen, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb. Jeffrey L. Wolf reports consultancy for Adaptive Biotech, TeneoBio, Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Takeda, and Janssen. Samir Parekh reports consultancy for Foundation Medicine and research funding (institutional) from Celgene, Pfizer, and Karyopharm. Hearn J. Cho is employed by the Multiple Myeloma Research Consortium and reports research funding from Takeda, Celgene, and Genentech. Samira Ziti‐Ljajic is an employee of Sanofi. Ajai Chari reports consultancy for Secura Bio, Novartis, Amgen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Celgene, Antengene, Takeda, Janssen, and Karyopharm; has received research funding from Amgen, Array Biopharma, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Takeda, Novartis, Oncopeptides, Pharmacyclics, and Seattle Genetics; and is an advisory board member for Amgen, Celgene, Millennium/Takeda, Novartis, Janssen, Karyopharm, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Secura Bio, and Seattle Genetics. The other authors made no disclosures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isatuximab plus carfilzomib-dexamethasone versus carfilzomib-dexamethasone in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma (IKEMA): overall survival analysis of a phase 3, randomised, controlled trial.Lancet Haematol. 2024 Oct;11(10):e741-e750. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(24)00148-0. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Lancet Haematol. 2024. PMID: 39067465 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 1b study of isatuximab plus pomalidomide/dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.Blood. 2019 Jul 11;134(2):123-133. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-02-895193. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30862646 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase 1b study of isatuximab plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.Blood. 2017 Jun 22;129(25):3294-3303. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-09-740787. Epub 2017 May 8. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28483761 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Isatuximab: A Review of Its Use in Multiple Myeloma.Target Oncol. 2021 Sep;16(5):675-686. doi: 10.1007/s11523-021-00827-0. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Target Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34351561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isatuximab, carfilzomib and dexamethasone (Isa-Kd) for the management of relapsed multiple myeloma.Future Oncol. 2021 Dec;17(35):4849-4860. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0778. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34553603 Review.
Cited by
-
Isatuximab in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma: A Review and Comparison With Daratumumab.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221106563. doi: 10.1177/15330338221106563. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35903924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti CD38 monoclonal antibodies for multiple myeloma treatment.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2052658. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2052658. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35404740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-CD38 antibody therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: differential mechanisms of action and recent clinical trial outcomes.Ann Hematol. 2022 Oct;101(10):2123-2137. doi: 10.1007/s00277-022-04917-5. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Ann Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35943588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum hsa_circ_0087776 as a new oncologic marker for the joint diagnosis of multiple myeloma.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12447-12459. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005875. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34905439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Durer C, Durer S, Lee S, et al. Treatment of relapsed multiple myeloma: evidence‐based recommendations. Blood Rev. 2020;39:100616. - PubMed
-
- Lonial S, Weiss BM, Usmani SZ, et al. Daratumumab monotherapy in patients with treatment‐refractory multiple myeloma (SIRIUS): an open‐label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1551‐1560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

