Serum Amyloid A Protein as a useful biomarker to predict COVID-19 patients severity and prognosis
- PMID: 33735714
- PMCID: PMC7923863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107512
Serum Amyloid A Protein as a useful biomarker to predict COVID-19 patients severity and prognosis
Abstract
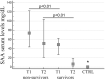
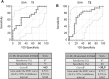
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) can present with different grades of severity from mild to critical. Evaluation of biomarkers predicting severity is crucial to identify patients at high risk of disease progression and poor prognosis. Serum Amyloid A (SAA) is an acute-phase protein mainly produced by the liver in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this study, we investigated SAA levels at admission (T1) and after 15 days (T2) of hospitalization in two groups of patients: survivors and non-survivors. At T1, the non-survivors showed higher SAA level than survivors (74 mg/dL vs 48.75 mg/dL). At T2, the survivor group value decreased to 6.55 mg/dL, the non-survivor group still showed high levels (51.1 mg/dL). The SAA level in control group was 0.35 mg/dL. Furthermore, a cut-off value of 63 mg/dL able to discriminate survivors from non-survivors was established by ROC curve analysis at T1. At T2, the cut-off decreased to 30.9 mg/dL. A similar decreasing trend was observed for D-Dimer, hsCRP, IL-6 and procalcitonin levels. The results of this retrospective study suggest that SAA is a good marker of COVID-19 disease alone and/or in combination with other inflammatory biomarkers. Identification of reliable prognostic analytes is of great clinical relevance, as it would improve patient management besides being costs saving.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2; Serum Amyloid A.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.L., Chen H.D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.D., Liu M.Q., Chen Y., Shen X.R., Wang X., Zheng X.S., Zhao K., Chen Q.J., Deng F., Liu L.L., Yan B., Zhan F.X., Wang Y.Y., Xiao G.F., Shi Z.L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579:270–273. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-29 December 2020, 2020.
-
- Lippi G., Plebani M. The critical role of laboratory medicine during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and other viral outbreaks. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019;58(2020):1063–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

