Two Cases of Possible Familial Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in a Family with Extensive History of Cancer
- PMID: 33735874
- PMCID: PMC8448803
- DOI: 10.1159/000513925
Two Cases of Possible Familial Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in a Family with Extensive History of Cancer
Abstract
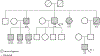
CML is defined by the presence of an oncogenic fusion protein caused by a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9q and 22q. While our molecular understanding of CML pathogenesis has revolutionized drug development for this disease, we have yet to identify many predisposing factors for CML. Familial occurrence of CML has been rarely reported. Here, we describe 2 cases of CML in a 24-year-old woman and in her 73-year-old maternal great aunt. We describe genetic variants in these patients and report on their environmental exposures that may have contributed to CML pathogenesis. The possible familial association of these 2 cases of CML warrants further investigation into more definitive etiologies of this disease.
Keywords: Chronic myeloid leukemia; Familial cancer; Hereditary cancer syndromes.
© 2021 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Rowley JD. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973June1;243(5405):290–3. - PubMed
-
- Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985June13–19315(6020):550–4. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006December7;355(23):2408–17. - PubMed
-
- Ross DM, Branford S, Seymour JF, Schwarer AP, Arthur C, Yeung DT, et al. Safety and efficacy of imatinib cessation for CML patients with stable undetectable minimal residual disease: results from the TWISTER study. Blood. 2013July25;122(4):515–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

