Epidemiological survey to determine the prevalence of cholecystolithiasis in Uyghur, Kazakh, and Han Ethnic Groups in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China: cross-sectional studies
- PMID: 33736598
- PMCID: PMC7977306
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01677-w
Epidemiological survey to determine the prevalence of cholecystolithiasis in Uyghur, Kazakh, and Han Ethnic Groups in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China: cross-sectional studies
Abstract
Background: This study was performed to understand the prevalence of and possible risk factors for cholecystolithiasis in Uyghur, Kazakh, Han, and other ethnic groups in the Xinjiang Uyghur autonomous region of China.
Methods: Subjects were enrolled using typical case sampling and multistage stratified random sampling. We collected epidemiological data regarding cholecystolithiasis using a standard questionnaire of risk factors for gallbladder disease in Xinjiang. The subjects completed the questionnaire and underwent an abdominal ultrasound examination of the liver and gallbladder.
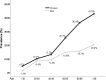
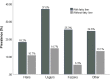
Results: This study included 5454 Xinjiang residents aged ≥ 18 years. The prevalence of cholecystolithiasis was 15% (11.3% in men and 17.1% in women), and the sex difference was statistically significant (male-to-female odds ratio [OR] 1.867; p < 0.001). The cholecystolithiasis prevalence was also significantly different among the Han, Uyghur, Kazakh, and other ethnic groups (13.1%, 20.8%, 11.5%, and 16.8%, respectively; p < 0.001). The prevalence of cholecystolithiasis in northern Xinjiang was 13.5% and that in southern Xinjiang was 17.5%; this difference was also statistically significant (OR 1.599; p < 0.001). Across all ethnic groups, the cholecystolithiasis prevalence significantly increased with age (all p < 0.01) and body mass index (BMI) (all p < 0.01). A multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that cholecystolithiasis prevalence was associated with sex, age, BMI, smoking, diabetes, fatty liver disease, and geographical differences between northern and southern Xinjiang.
Conclusions: The prevalence of cholecystolithiasis was significantly higher in the Uyghur ethnic group than in the Han, Kazakh, and other ethnic groups; in women than in men; in southern Xinjiang than in northern Xinjiang; in patients with fatty liver disease; and increased with age and BMI. Our findings could provide a theoretical basis for the formulation of control measures for cholecystolithiasis.
Keywords: Cholecystolithiasis; Epidemiology; Prevalence; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shi J, Liu S, Xie W. Risk factors of cholelithiasis in China: a meta-analysis. Chin J Gastroenterol. 2005;10(4):217–222.
-
- Zhu XY, Gao FJ, Li R, et al. Prevalence of cholelithiasis and associated risk factors among adult population in Shanghai. J Clin Hepatol. 2010;26(6):646–650.
-
- Zong B, Ai ZZ, Xu JZ, Mei XR, Wu RX, Hou BG, et al. Investigation of prevalent rate of gallstone in Wensu County of Xinjiang. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg. 2006;12(3):159–160.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources