High-elevational occurrence of two tick species, Ixodes ricinus and I. trianguliceps, at their northern distribution range
- PMID: 33736666
- PMCID: PMC7977262
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-021-04604-w
High-elevational occurrence of two tick species, Ixodes ricinus and I. trianguliceps, at their northern distribution range
Abstract
Background: During the last decades a northward and upward range shift has been observed among many organisms across different taxa. In the northern hemisphere, ticks have been observed to have increased their latitudinal and altitudinal range limit. However, the elevational expansion at its northern distribution range remains largely unstudied. In this study we investigated the altitudinal distribution of the exophilic Ixodes ricinus and endophilic I. trianguliceps on two mountain slopes in Norway by assessing larval infestation rates on bank voles (Myodes glareolus).
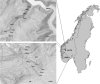
Methods: During 2017 and 2018, 1325 bank voles were captured during the spring, summer and autumn at ten trapping stations ranging from 100 m to 1000 m.a.s.l. in two study areas in southern Norway. We used generalized logistic regression models to estimate the prevalence of infestation of both tick species along gradients of altitude, considering study area, collection year and season, temperature, humidity and altitude interactions as extrinsic variables, and host body mass and sex as intrinsic predictor variables.
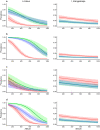
Results: We found that both I. ricinus and I. trianguliceps infested bank voles at altitudes up to 1000 m.a.s.l., which is a substantial increase in altitude compared to previous findings for I. ricinus in this region. The infestation rates declined more rapidly with increasing altitude for I. ricinus compared to I. trianguliceps, indicating that the endophilic ecology of I. trianguliceps may provide shelter from limiting factors tied to altitude. Seasonal effects limited the occurrence of I. ricinus during autumn, but I. trianguliceps was found to infest rodents at all altitudes during all seasons of both years.
Conclusions: This study provides new insights into the altitudinal distribution of two tick species at their northern distribution range, one with the potential to transmit zoonotic pathogens to both humans and livestock. With warming temperatures predicted to increase, and especially so in the northern regions, the risk of tick-borne infections is likely to become a concern at increasingly higher altitudes in the future.
Keywords: Altitude; Bank vole; Distribution; Ixodes ricinus; Ixodes trianguliceps; Myodes glareolus; Range shift; Ticks.
Conflict of interest statement
All contributing authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest involved in this study.
Figures


References
-
- Garcia-Vozmediano A, Krawczyk AI, Sprong H, Rossi L, Ramassa E, Tomassone L. Ticks climb the mountains: ixodid tick infestation and infection by tick-borne pathogens in the Western Alps. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2020;1:101489. - PubMed
-
- Tombre IM, Oudman T, Shimmings P, Griffin L, Prop J. Northward range expansion in spring-staging barnacle geese is a response to climate change and population growth, mediated by individual experience. Glob Change Biol. 2019;25(11):3680–3693. - PubMed
-
- Osland MJ, Feher LC. Winter climate change and the poleward range expansion of a tropical invasive tree (Brazilian pepper—Schinus terebinthifolius) Glob Change Biol. 2020;26(2):607–615. - PubMed
-
- Rubidge EM, Patton JL, Lim M, Burton AC, Brashares JS, Moritz C. Climate-induced range contraction drives genetic erosion in an alpine mammal. Nat Clim Change. 2012;2(4):285–288.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

