Galectin-3 in septic acute kidney injury: a translational study
- PMID: 33736691
- PMCID: PMC7977587
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-021-03538-0
Galectin-3 in septic acute kidney injury: a translational study
Abstract
Background: Galectin-3 (Gal-3) is a pleiotropic glycan-binding protein shown to be involved in sepsis and acute kidney injury (AKI). However, its role has never been elucidated in sepsis-associated AKI (S-AKI). We aimed to explore Gal-3's role and its potential utility as a therapeutic target in S-AKI.
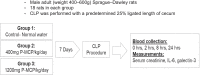
Methods: In 57 patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with sepsis, serum Gal-3 was examined as a predictor of ICU mortality and development of AKI. In a rat model of S-AKI induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), 7-day mortality and serum Gal-3, Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and creatinine were examined at 2, 8, and 24 hours (h) post-CLP. Two experimental groups received the Gal-3 inhibitor modified citrus pectin (P-MCP) at 400 mg/kg/day and 1200 mg/kg/day, while the control group received water only (n = 18 in each group).
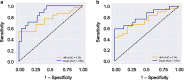
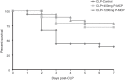
Results: Among 57 patients, 27 developed AKI and 8 died in the ICU. Serum Gal-3 was an independent predictor of AKI (OR = 1.2 [95% CI 1.1-1.4], p = 0.01) and ICU mortality (OR = 1.4 [95% CI 1.1-2.2], p = 0.04) before and after controlling for age, AKI, and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE II) score. In the CLP rat experiment, serum Gal-3 peaked earlier than IL-6. Serum Gal-3 was significantly lower in both P-MCP groups compared to control at 2 h post-CLP (400 mg: p = 0.003; 1200 mg: p = 0.002), and IL-6 was significantly lower in both P-MCP groups at all time points with a maximum difference at 24 h post-CLP (400 mg: p = 0.015; 1200 mg: p = 0.02). In the Gal-3 inhibitor groups, 7-day mortality was significantly reduced from 61% in the control group to 28% (400 mg P-MCP: p = 0.03) and 22% (1200 mg P-MCP: p = 0.001). Rates of AKI per RIFLE criteria were significantly reduced from 89% in the control group to 44% in both P-MCP groups (400 mg: p = 0.007; 1200 mg: p = 0.007).
Conclusions: This translational study demonstrates the importance of Gal-3 in the pathogenesis of S-AKI, and its potential utility as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Galectin-3; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
IE is the developer of P-MCP. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The role of phospholipid transfer protein in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Crit Care. 2025 Jan 20;29(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13054-025-05253-6. Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 39833975 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury and inflammatory response of sepsis following cecal ligation and puncture in d-galactose-induced aging rats.Clin Interv Aging. 2017 Mar 29;12:593-602. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S132277. eCollection 2017. Clin Interv Aging. 2017. PMID: 28408808 Free PMC article.
-
A translational study of Galectin-3 as an early biomarker and potential therapeutic target for ischemic-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury.J Crit Care. 2021 Oct;65:192-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.06.013. Epub 2021 Jul 2. J Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34225083
-
The prognostic utility of galectin-3 in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a scoping review.Biomarkers. 2024 Nov;29(7):485-493. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2024.2415073. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Biomarkers. 2024. PMID: 39422445
-
Sepsis and acute kidney injury.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Jun;22(6):999-1006. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010050484. Epub 2011 May 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21566052 Review.
Cited by
-
The efficiency of blood cell counts and inflammatory indices in prediction of need for acute kidney injury in patients with crush syndrome.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 26;26(1):417. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04318-6. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40713512 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 Mediates Endotoxin Internalization and Caspase-4/11 Activation in Tubular Epithelials and Macrophages During Sepsis and Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury.Inflammation. 2024 Feb;47(1):454-468. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01928-w. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 37979076
-
Galectin-3 in Kidney Diseases: From an Old Protein to a New Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 14;23(6):3124. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063124. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On Whether Ca-125 Is the Answer for Diagnosing Overhydration, Particularly in End-Stage Kidney Disease Patients-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 12;25(4):2192. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042192. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396869 Free PMC article.
-
The potential roles of galectin-3 in AKI and CKD.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1090724. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1090724. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36909244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Uchino S, Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Septic acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: clinical characteristics and outcomes. CJASN. 2007;2:431–439. - PubMed
-
- Hoste EA, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Cely CM, Colman R, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:1411–1423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

