Effects of Diet and Exercise-Induced Weight Loss on Biomarkers of Inflammation in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 33737299
- PMCID: PMC8172485
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1029
Effects of Diet and Exercise-Induced Weight Loss on Biomarkers of Inflammation in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Adiponectin, leptin, and pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines are implicated in breast cancer risk and recurrence. Weight loss, via the dynamic interplay of energy balance through exercise and/or caloric restriction, decreases risk of breast cancer recurrence.
Methods: We investigated the effects of lifestyle modifications (exercise only, or combined caloric restriction and exercise) on adipokines, IL2, IL6, IL8, IL10, C-reactive protein (CRP), and TNFα biomarkers in breast cancer survivors. Searches were completed in June and July of 2019 to identify randomized controlled trials that met inclusion criteria. Weighted mean difference was calculated using random- or fixed-effects models based on the heterogeneity of the studies.
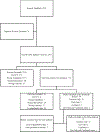
Results: 2501 records were identified, with 30 ultimately meeting inclusion criteria of the systematic review; 21 studies provided data suitable for meta-analysis. We observed leptin levels were significantly reduced in the exercise-only group compared with sedentary control [WMD -5.66; 95% confidence interval (CI), -11.0 to -0.33; P = 0.04].
Conclusions: Leptin may be a primary mediator of exercise-induced improvements in breast cancer recurrence.
Impact: This is the first review and meta-analysis to examine combined exercise and caloric restriction programs in breast cancer survivors. Future studies should further examine combined programs and their efficacy for altering leptin.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. U.S. Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool, based on November 2017 submission data (1999–2015). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute; <https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/DataViz.html.> Accessed 2019.
-
- Argolo DF, Hudis CA, Iyengar NM. The Impact of Obesity on Breast Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 2018;20:47. - PubMed
-
- Crespi E, Bottai G, Santarpia L. Role of inflammation in obesity-related breast cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2016;31:114–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

